Parts of Speech: English Grammar Guide with Examples

Some grammar sources classify English into 8 parts of speech. Some sources say that there are 9. Here at ESLBlock.com, we explain the most recent categorization system as 10 parts of speech.
We can classify English words into ten types referred to as “parts of speech” or “word classes.” It’s crucial to know the different parts of speech. This allows you to analyze sentences and comprehend the meaning behind them. It also assists you in making excellent sentences.
Every word is part of speech. The phrase “part of speech” refers to the function a word plays in sentences. Like every other show or workplace with an ensemble cast, the roles were designed to be interconnected.
- What Are Parts Of Speech?
- Importance of Parts of Speech in English Grammar
- Words and lexemes
- Open and Closed Word Classes
- Explanation of Different Parts of Speech (with Examples)
- 1. Nouns (n.)
- 2. Verbs (vb.)
- 3. Pronoun (pron.)
- 4. Adjective (adj.)
- 5. Adverb (adv.)
- 6. Preposition (prep.)
- 7. Conjunction (conj.)
- 8. Interjection (interj.)
- 9-10. Articles and Determiners
- Parts of Speech in English – Printable Infographic
- Parts of Speech in English – Printable Flashcards
- Parts of Speech in English MCQs Test
Parts of speech are classifications of words that perform similar roles in grammatical terms in phrase and sentence structure. So what exactly are various parts of speech? And what do you know about which words are related to different grammar categories? This article will describe the various parts of speech and show you how to recognize them and alter and utilize them in both complicated and straightforward sentences.
Within the English language, there are many parts of speech that are arranged to create sentences. Without these elements, the language wouldn’t be able to work.
Learn more about the different parts of speech, the words we use each day, and how to convey ideas effectively.
What Are Parts Of Speech?
The parts of speech comprise categories determined by the role they play in sentence structure. The word categories are arranged according to their function in grammatical terms and the meanings they create and communicate.
Within the English language, there are about ten common speech parts. They include nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, articles, conjunctions, interjections, determiners, and pronouns.
Although the meanings of these categories will be explained in the following sections, remember that these words are grammatically relevant or perform as grammatical elements in the speech, including sentence structure and meaning.

Importance of Parts of Speech in English Grammar
1. Clarity and Precision
Parts of speech play a crucial role in enhancing the clarity and precision of communication. By assigning specific roles to words, such as nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs, speakers and writers can convey their thoughts with greater accuracy. This precision ensures that the intended meaning is effectively communicated, reducing the likelihood of misinterpretation.
2. Sentence Structure
Understanding and applying the different parts of speech is essential for constructing grammatically correct and well-structured sentences. Each part of speech contributes to the overall syntax, determining how words relate to each other within a sentence. Proper sentence structure is fundamental for effective communication and is a key aspect of mastering English grammar.
3. Expressive Language
Parts of speech contribute to the expressiveness of language. Adjectives and adverbs, for example, allow speakers and writers to add detail, emphasis, and nuance to their expressions. By utilizing the various parts of speech effectively, individuals can convey emotions, paint vivid images, and create a more engaging and dynamic language experience.
4. Consistent Usage
Consistency in the use of parts of speech is vital for maintaining coherence in written and spoken language. Adhering to established rules and conventions ensures that the message is conveyed in a way that is both comprehensible and grammatically sound. Consistent use of parts of speech also contributes to the overall flow and rhythm of the language.
5. Grammatical Analysis
Parts of speech form the foundation for grammatical analysis and understanding. Proficiency in identifying and categorizing words into their respective parts of speech is essential for advanced language skills, including syntax analysis, sentence parsing, and the ability to critically assess and improve one’s own writing. A solid grasp of parts of speech is, therefore, a cornerstone of mastering English grammar.
Words and lexemes
In linguistics, we distinguish lexemes and words. Words are an everyday word that is used by all of us every day. For example, every one of us will be able to agree on the number of words that appear in this sentence:
Amelia ran 9 kilometers yesterday, but she’s only running 3 today. (11 words)
When we examine the situation more closely at the details, we can see that ran and running are derived from run, which is the exact verb. Both words are variations from the same word. The run is lexeme which is a simple version of the term.
Open and Closed Word Classes
Open Classes: Open classes allow new members through borrowing (for example, the noun cafe) and derivation (for example, the adjective bounteous from the noun bounty). Open classes of words include:
- Nouns
- Verbs
- Adjectives
- Adverbs
Closed Classes: Closed classes of words do not allow new members and usually involve grammatical rather than lexical terms. Closed classes of words include:
- Determiners
- Prepositions
- Coordinators
- Subordinators
Explanation of Different Parts of Speech (with Examples)
This chapter will look a bit more closely at the various components of speech like the verb, noun, and adjective. This will enable us to understand better how sentences are constructed and how all the parts of speech function.
1. Nouns (n.)
We can define a noun as, a noun which is a word that names person, place, object or concept. In general, anything that names a “thing” is a noun regardless of whether it’s a basketball court in San Francisco, Cleopatra, or self-preservation. There are many different subcategories of nouns, such as the proper noun collective noun, the possessive noun, and the common noun. Each has a distinct function, so let’s examine this in greater detail.
Noun Examples
Ball, Jeffrey, cat, Korea, pen, mother, New Year, Lahore, dog, cat, elephant, bat, garden, school, Eid, work, music, town, America, Manila, teacher, Madinah, farmer, Bob, Sean, feet, Michael, police officer, air, France, coffee, football, danger, classroom, happiness wedding, Christmas.
Noun example sentences
- I live in America.
- Amelia is my sister.
- I love to play with my cat.
- The name of this dog is Jake.
- Atlantic Ocean is very beautiful.
- The capital of England is London.
- Albert Einstein was born in Germany.
- Cara and Bobby are close friends.
- Every Sunday John visits the church.
- I love to collect storybooks.
Common Noun
Common nouns are the simplest form of nouns. Common nouns are words of naming that are commonly used by objects, people, and animals. Common nouns don’t refer to any specific individual, location or thing. They are general terms. Therefore, they cannot be capitalized unless they are used to begin an entire sentence. For instance, girl, boy doctor, town, city dog, car and others.
- Kristen has a cup.
- Do you want a pen?
Proper Noun
Names of people or places such as your name, your sister’s name, your mother parents. You may visit detailed article about Proper Nouns.
- My name is David.
- My mother’s name is Sofie.
- I visited California.
Collective Noun
Collective nouns are used to name a group of persons, places, animals or things. For example, a flock of sheep, a swarm of bees and a team of players.
- A shoal of fish.
- A herd of cattle.
- An army of soldiers.
Possessive Noun
A possessive noun refers to a word that identifies who or what owns something. We can add an apostrophe (‘s) to make most singular nouns possessive form.
- This is William’s pen. (Means – The pen belongs to William)
- Sophia’s homework was checked.
2. Verbs (vb.)
Verbs are words used to describe what happens (action) in the sentence. They can also show a sentence subject’s state of being (is, was). Verbs alter their form depending on the tense (present or past) and the distinction between count (singular and plural).
Verb examples
run, wash, sing, congratulate, dance, believe, seem to, finish, eat, complete, drink, play, become, help.
| First Form | Second Form | Third Form |
|---|---|---|
| Eat | Ate | Eaten |
| Run | Ran | Run |
| Write | Wrote | Written |
| Speak | Spoke | Spoken |
| Sing | Sang | Sung |
| Dance | Danced | Danced |
| Sleep | Slept | Slept |
| Go | Went | Gone |
| See | Saw | Seen |
| Do | Did | Done |
| Have | Had | Had |
| Make | Made | Made |
| Take | Took | Taken |
| Give | Gave | Given |
| Come | Came | Come |
| Read | Read | Read |
| Speak | Spoke | Spoken |
| Drive | Drove | Driven |
| Break | Broke | Broken |
| Swim | Swam | Swum |
Verb example sentences
- Amelia is playing the football.
- We bought a new dog.
- The roof on the shop leaks.
- The lightning struck the tower.
- Will you help me with the kitchen?
- She rode her new bike around the block for an hour.
- The dog sat by the gate.
- I’ll play this song on my guitar.
- She thought about her stupid mistake in the exam.
- John visited his friend for a while and then went market.
- She danced gracefully at the party last night.
- The sun rises early in the morning.
- I read an interesting book over the weekend.
- They spoke passionately about their travel experiences.
- The chef cooked a delicious meal for the guests.
- He runs five miles every day for his fitness.
- The children played happily in the park.
- We sang our favorite songs together at the concert.
- She writes poetry in her free time.
- The cat sleeps peacefully on the windowsill.
Kinds of Verbs
A verb is a necessary part of a sentence and is known as the soul of the English language. Following are the various kinds of verbs.
- Regular verbs
- Irregular verbs
- Modal verbs
- Dynamic verbs
- Auxiliary verbs
- Stative verbs
- Linking Verbs
- Transitive Verbs
- Finite Verbs
- Infinitive Verbs
- Intransitive Verbs
- Causative verbs
Explore the full list of verbs from A to Z
- Verbs That Start With A
- Verbs That Start With B
- Verbs That Start With C
- Verbs That Start With D
- Verbs That Start With E
- Verbs That Start With F
- Verbs That Start With G
- Verbs That Start With H
- Verbs That Start With I
- Verbs That Start With J
- Verbs That Start With K
- Verbs That Start With L
- Verbs That Start With M
- Verbs That Start With N
- Verbs That Start With O
- Verbs That Start With P
- Verbs That Start With Q
- Verbs That Start With R
- Verbs That Start With S
- Verbs That Start With T
- Verbs That Start With U
- Verbs That Start With V
- Verbs That Start With W
- Verbs That Start With X
- Verbs That Start With Y
- Verbs That Start With Z
3. Pronoun (pron.)
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. The noun substituted by a pronoun can be known as an antecedent. For example, in the sentence, I love my bunny because he is a good boy, the word he in the sentence is a pronoun that replaces the noun bunny.
In grammatical terms, pronouns behave like nouns. They can be used for subjects and objects; They refer to persons, places, and things; they can be plural or singular.
Pronoun Examples
I, me, you, yours, he, himself, she herself, it, its, we, they, us, them, who, what, this, that, anyone, nobody, something.
Pronoun Example Sentences
- We looked for Sofia at her house, but she wasn’t there.
- I took my bike to the mechanic to get it repaired.
- This is the best evening ever!
- Someone donated $1500 to our charity.
- Kristen thinks that mayonnaise goes well with anything.
- Oliver isn’t at work this week; he‘s gone on holiday.
- Tell her the truth.
- Isabella tried it herself.
- They can’t blame him for everything.
- The man who called yesterday wants to buy the car.
Kinds of Pronouns
There are many kinds of pronouns we can use in our writing and speech. First, we will briefly discuss the various types. Then, if you’d like to look into each of them in greater depth, we’ve provided comprehensive information on each of the pronouns.
- Personal pronouns
- Possessive pronouns
- Relative pronouns
- Reflexive pronouns
- Indefinite pronouns
- Interrogative pronouns
- Demonstrative pronouns
- Reciprocal pronouns
- Intensive pronouns
4. Adjective (adj.)
The word is used to enhance the meaning of a noun and pronoun, more simply we use adjectives to add something to the meaning of the noun. For example, we understand the meaning of the word “boy”. But, boy+ intelligent is a different thing from boy + stupid. In the same way, boy + beautiful refers to something different than boy + ugly. The word “boy” is used to mean exactly the same thing in every sentence. However, the adjectives, intelligent, stupid, beautiful and ugly define the meaning of the word “girl” completely different.
Adjective Examples
Adorable, adventurous, aggressive, agreeable, alert, alive, amused, angry, annoyed, annoying, anxious, fast, cool, dry, blue, smart, short, heavy, hot, green, red, interesting, large.
Adjective Example Sentences
- I have a tall dog. (The word ‘tall’ is describing an attribute of the dog)
- She is smart. (The word ‘smart’ is providing information about the subject)
- The hungry ducks are crying.
- I saw a flying crow.
- This is a white bag.
- The large squirrel ran up the wall.
- My sister has long hair.
- The sky became dark.
- Her story seemed interesting.
- Furry cats may overheat in the summertime.
Kinds of Adjective
Here, we will briefly look at 13 different types of adjectives. If you’d like to know more about each adjective more in-depth You can go through our entire guide to the various kinds of adjectives!
- Possessive adjectives
- Comparative adjectives
- Superlative adjectives
- Descriptive adjectives
- Predicate adjectives
- Compound adjectives
- Demonstrative adjectives
- Proper adjectives
- Participial adjectives
- Limiting adjectives
- Interrogative adjectives
- Distributive adjective
- Attributive adjectives
5. Adverb (adv.)
An adverb is used to describe or further explain an adjective, verb, or another adverb but never a noun. They can add more information to a sentence making it more transparent and more accessible for the listener to imagine what is being described in detail. Adverbs will often end in the letters -ly, but there are exceptions to this rule, such as the words very and never.
Adverbs specify when, where, how, and why something happened and to what extent or how often.
Adjective Examples
Softly, neatly, lazily, very, badly, fully, often, only, nearly, hungrily, hopefully, softly, silently, well, really, sometimes
Adjective Example Sentences
- Amelia speaks loudly. (How does Amelia speak?)
- Afterwards he smoked a cigarette. (When did he smoke?)
- Mia lives locally. (Where does Mia live?)
- This is an extremely attractive girl.
- They have a very large cat.
- Tom boat did not run badly.
- William is very fat.
- Fortunately, Sofia recorded William’s win.
- Her car drives quickly.
- The baby is crying loudly.
6. Preposition (prep.)
Prepositions are a common word. Seven of them are among the top 20 most used words in English. Prepositions connect a word with other parts of the sentence. They explain the connection is, e.g. in time or space.
A preposition is used in English to establish a relationship between two phrases or words. Words like in, prior, to, on at, in between, before, on, at etc., are examples of prepositions.
A preposition is a word put before a noun or pronoun to create an expression that modifies another phrase. Thus, a preposition is always an element of a prepositional phrase. The prepositional phrase usually is used as an adjective or an adjective, or an adverb.
Preposition Examples
About, above, across, after, against, along, among, at, before, by, for, from, in, inside, into, of, on, onto, over, to, up, with.
Preposition Example Sentences
- The dog is sitting on the table.
- I am going to the salon after my lunch.
- We are running in the gym.
- The moon is above the clouds.
- I read that news in the newspapers.
- Cat was hiding under the table.
- She drove over the bridge.
- She lost her bracelet at the beach.
- The grammar book belongs to David.
- We were sitting by the tree.
7. Conjunction (conj.)
Conjunctions are words used to connect words, phrases, and clauses. There are many different conjunctions within the English language. However, some commonly used ones include and or, but for, if, and when.
Conjunction Examples
Whether, and, however, still, or, so, after, yet, since, before, either, neither, because, unless, as, because, but, for, just as, nor, not only.
Conjunction Example Sentences
- My girlfriend and I are going on a date.
- Sofia will go to the shop but not before she has had something to eat.
- He was tired yet he still went to the gym.
- I tried to hit the thumb but hit my nail instead.
- I have two dogs and a goldfish.
- She’d like a bike for commuting to work.
- They can have apple ice cream or a brownie sundae.
- Neither the red dress nor the white one looks right on her.
- My husband always worked hard so we could afford the car we wanted.
- They can watch movie provided they disturb nobody.
Types of Conjunction
Many different kinds of conjunctions can perform various tasks within sentence structures. This includes:
8. Interjection (interj.)
An interjection is defined as “An interjection or exclamation is a word used to express a particular emotion or sentiment on the part of the speaker.”
Interjection Examples
Oh!, Wow!, oops!, Ahem!, aha!, gosh!, aw!, great!, hey!, hi!, hooray!, yeah!, phew!, eh!, ouch!, hi!, well!
Interjection Example Sentences
- Good! now we can celebrate the wedding party.
- Wow! did they see how big that elephant was?
- Hooray! Amelia passed her exam!
- Oh, what’s an apple.
- Hey! get out of the room!
- Yes! I can do it.
- Congrats! You finally got your bachelor’s degree.
- Phew! that was a close call.
- No! I run so short.
- Well, what did you say?
Types of Interjection
You can use a verb, a noun, or an adverb as an interjection.
- Noun as an interjection
- Verb as an interjection
- Adverb as an interjection
9-10. Articles and Determiners
Determiners and articles act as adjectives by changing nouns, but they differ from adjectives because they are required for sentences to have the correct syntax.
Articles and determiners are two parts of speech used alongside noun phrases or nouns to help clarify their meaning.
Certain grammars of the past have considered the article as a distinct component of speech. However, modern grammars generally include articles in the class that are determiners that define or quantify a word.
Articles and Determiner Examples
- Numbers: three, seven, ninety-nine
- Distributives: neither, either, half, both, every, each, all
- Pronouns and possessive determiners: her, his, its, your, their, my, our
- Difference determiners: another, the other, other
- Demonstratives: this, that, these, those
- Quantifiers: a few, a little, much, many, some, most, any, enough
- Pre-determiners: such, quite, rather, what.
- Articles: the, a, an
Articles and Determiner Example Sentences
- All nations want to be free.
- I saw an accident of a bike.
- These are dogs.
- My family is a very happy.
- They have a lot of people on Pinterest.
- You have five days left to complete that project.
- Sorry, I’m too busy, I have other job to do.
- Amelia saw a star last night.
- William saw the moon last night.
- Sophia has a beautiful doll.
Parts of Speech in English – Printable Infographic
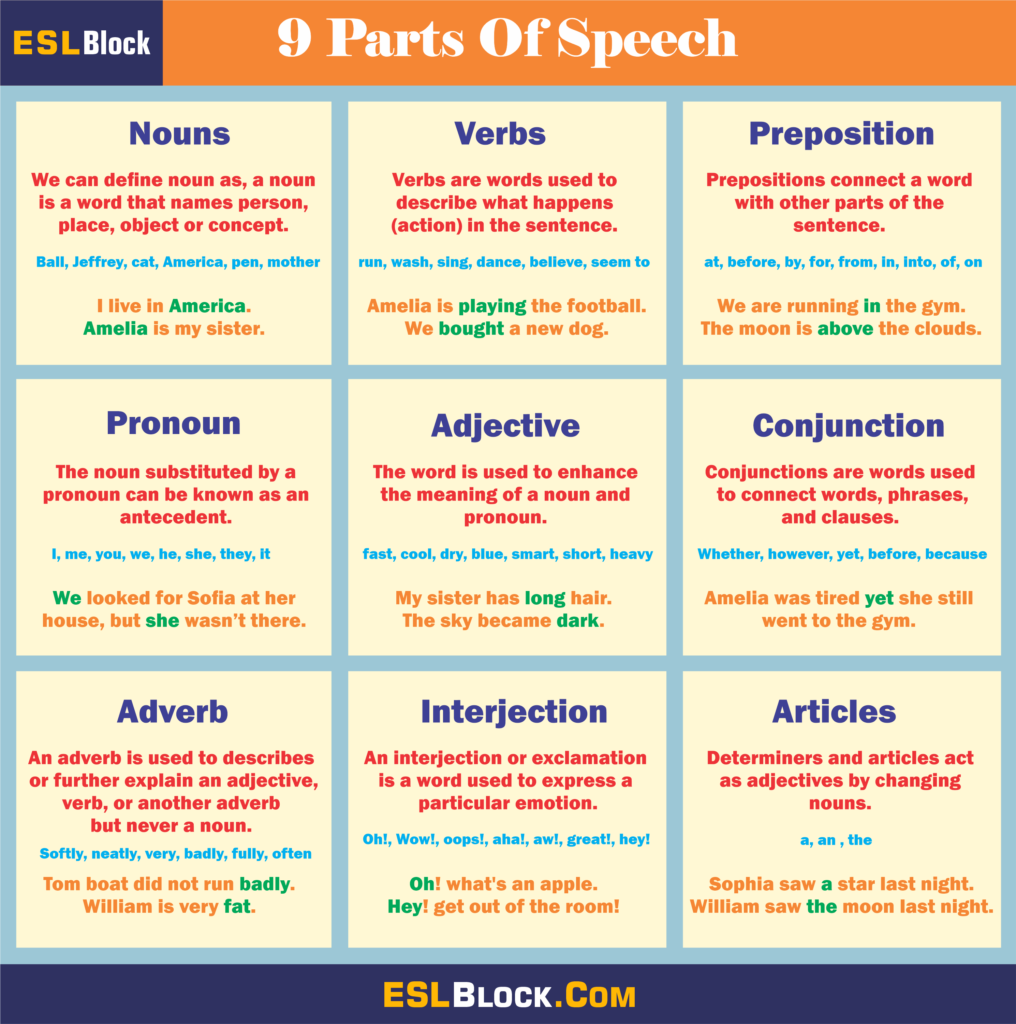
In the English language, there are eight parts of speech. Each one has its use. Without them, we’d not be able to form coherent sentences, so it is essential to be aware of the different functions each one serves. In these infographics, we’ll examine each of the different speech parts and what they are utilized for, as well as some illustrations of ways they are used in the context of a sentence.
Infographics are a fantastic way of conveying lots of details in a brief period in a way that’s exciting. Parts of speech infographics are a great way to help students and teachers communicate their thoughts and show how they learn—download parts of speech infographics right now.
Parts of Speech in English – Printable Flashcards
Parts of speech in English are often tricky to recognize in the context of a sentence. This flashcard set can help you understand the meaning of what a part of speech is and how the various parts of speech function in performing their tasks in a sentence. This set of flashcards can aid you in identifying and describing the eight parts of speech, as well as the roles they perform in sentences.
Parts of Speech in English MCQs Test
Make use of these parts of the speech quiz to test your English Grammar skills or your students. Answers are listed at the end of the page. Have fun!
You can take this grammar test online as well as print it on paper. It will test what you have learned from the Parts of Speech page.






[…] ALSO READ: Parts of Speech […]
I for all time emailed this web site post page to all my friends,
as if like to read it after that my contacts will too.
[…] For example, you might use something like to describe a student “He is a student.” If you want to include an adjective in the sentence, you could convey clearer information of what you are trying to tell by saying something like “He is an intelligent student.” or “He is a good student.” An adjective is one of the nine parts of speech. […]
[…] It’s impossible to live in a universe without nouns. Nouns love to be decorated somehow, which is why adjectives are involved. They’re interesting and vibrant. We’ve got the standard descriptors such as “Bad” and “Best.” An adjective is one of the nine parts of speech. […]
[…] It’s impossible to live in a universe without nouns. Nouns love to be decorated somehow, which is why adjectives are involved. They’re interesting and vibrant. We’ve got the standard descriptors such as “authentic” and “attentive.” An adjective is one of the nine parts of speech. […]
[…] It’s impossible to live in a universe without nouns. Nouns love to be decorated somehow, which is why adjectives are involved. They’re interesting and vibrant. We’ve got the standard descriptors such as “authentic” and “attentive.” An adjective is one of the nine parts of speech. […]
I think this is among the most vital info for me. And i’m glad reading your article.
But want to remark on some general things, The site
style is great, the articles is really great : D. Good job, cheers
Hello there! This is kind of off topic but I need some help from an established blog.
Is it very difficult to set up your own blog? I’m not
very techincal but I can figure things out pretty quick.
I’m thinking about making my own but I’m not sure where
to begin. Do you have any points or suggestions? Appreciate it
It’s amazing to pay a quick visit this website and reading the views of
all mates concerning this post, while I am also eager of getting familiarity.
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you design this
website yourself or did you hire someone to
do it for you? Plz answer back as I’m looking to create my own blog and would like to find out
where u got this from. kudos
What’s up Dear, are you really visiting this web page regularly, if so afterward you will absolutely obtain nice know-how.
At this time I am going to do my breakfast, once having my breakfast coming yet again to read additional news.
I got this web page from my buddy who shared with me
concerning this site and at the moment this time I am browsing this website and reading very informative content at this
place.
It’s enormous that you are getting thoughts from this article as well as from our argument made at this place.
You could certainly see your enthusiasm in the paintings you write. The sector hopes for even more passionate writers like you who aren’t afraid to say how they believe. All the time follow your heart. “He never is alone that is accompanied with noble thoughts.” by Fletcher.
Great ?V I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your site. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs as well as related info ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, website theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Nice task..
I¦ve recently started a blog, the information you provide on this web site has helped me greatly. Thanks for all of your time & work.
Do you mind if I quote a few of your posts as long as I provide credit and sources back to your blog? My blog is in the exact same area of interest as yours and my visitors would genuinely benefit from some of the information you present here. Please let me know if this ok with you. Thank you!
Thank you for sharing your info. I truly appreciate your
efforts and I am waiting for your further post thank you once again.
Hello! Someone in my Facebook group shared this site with us so I came to check it out.
I’m definitely enjoying the information. I’m bookmarking and will be tweeting this to my followers!
Superb blog and amazing design.
Do you mind if I quote a few of your posts as long as I provide credit and
sources back to your webpage? My blog site is in the very same niche as yours and my visitors would truly benefit from a lot of the
information you present here. Please let me know if this alright with you.
Thank you!
Hey there I am so glad I found your website, I really found you by error, while
I was browsing on Google for something else, Anyhow I am here now and would just
like to say thanks for a tremendous post and a all
round interesting blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to read it all at the
moment but I have bookmarked it and also added your RSS feeds, so when I
have time I will be back to read much more,
Please do keep up the excellent jo.
This guide on parts of speech is absolutely fantastic! I especially appreciate how you broke down the 10 different categories. It can get really confusing with all the varying counts out there, but your explanation makes it so clear and easy to follow. The examples for each section are incredibly helpful for solidifying the concepts. I’m wondering, for advanced learners, are there any common pitfalls or specific parts of speech that tend to be more challenging to master than others?