Crocodiles of The World

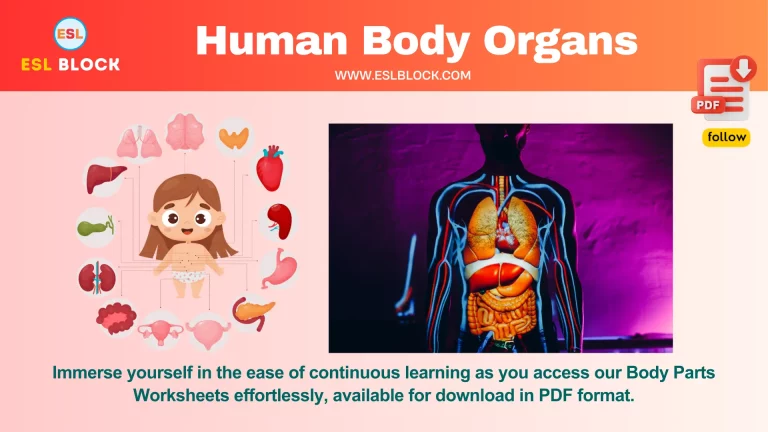
Crocodiles are a group of different large, aquatic reptiles that live in the tropics and subtropics. There are 23 species of crocodilians of the world, which include crocodiles, alligators, caimans, and gharials.
Crocodiles are apex predators and play an important role in their ecosystems. They are threatened by habitat loss, poaching, and climate change. Some of the largest crocodile species include the saltwater crocodile, Nile crocodile, and American crocodile.
All these crocodiles of the world are verified, using acknowledged sources for their genuineness, before being enlisted. Source: World’s Crocodiles.
Read also: List of Pet Animals
Difference between Crocodile and Alligator
Crocodiles and alligators are both reptiles that belong to the order Crocodilia. Although they may look similar at first glance, there are several key differences between the two. Here are five points of difference:
- Habitat: Crocodiles and alligators live in different parts of the world. Crocodiles are found in Africa, Asia, Australia, and the Americas, while alligators are found only in the Americas, primarily in the southeastern United States.
- Snout shape: The easiest way to tell a crocodile apart from an alligator is by looking at their snouts. Crocodiles have a V-shaped snout, while alligators have a U-shaped snout. The shape of their snouts is related to their diet and the types of prey they catch.
- Teeth: Another difference between crocodiles and alligators is their teeth. Crocodiles have a more aggressive bite and can use their long, sharp teeth to catch larger prey, while alligators have shorter, blunter teeth and tend to eat smaller prey.
- Size: In general, crocodiles are larger than alligators. The largest crocodile species, the saltwater crocodile, can grow up to 23 feet long and weigh over 2,000 pounds, while the largest alligator species, the American alligator, grows up to 14 feet long and weighs up to 1,000 pounds.
- Behavior: Crocodiles and alligators also have different behaviors. Crocodiles are generally more aggressive and territorial than alligators, and they are known to be more active hunters. Alligators are more social and tend to live in groups, while crocodiles are often solitary.
How did crocodiles get their name?
The word “crocodile” comes from the ancient Greek word “krokódeilos”, which means “lizard with pebbled skin”. The term was later adopted into Latin as “crocodilus”, and from there it spread to other languages. The name is believed to refer to the bumpy or scaly appearance of the crocodile’s skin, which looks like a series of small stones or pebbles.
It’s interesting to note that in many cultures throughout history, crocodiles have been revered as powerful and fearsome creatures.
In ancient Egypt, for example, the crocodile was seen as a sacred animal and was even worshipped as a god. In many other cultures, crocodiles have been associated with strength, ferocity, and primal power. This may help explain why the name “crocodile” has such a potent and evocative connotation even today.
Also Check: Future Perfect Progressive Tense
General Features of Crocodiles of the World
- Crocodiles are large, semi-aquatic reptiles that belong to the family Crocodylidae.
- They have a broad, flattened snout, sharp teeth, powerful jaws, and armored skin.
- The size of crocodiles ranges from about 1.5 meters (5 feet) to over 6 meters (20 feet), depending on the species.
- There are 14 species of crocodiles, with a wide diversity of structures, including freshwater, saltwater, and dwarf crocodiles.
- Crocodiles are found in many parts of the world, including Africa, Australia, Asia, the Americas, and even in the southern United States.
- Some species of crocodiles are considered endangered due to habitat loss and hunting.
- Crocodiles have a long life span, with some living over 80 years.
- They have a complex social behavior, communication, and learning abilities.
- Crocodiles are good swimmers and can move quickly on land with a “high walk” gait.
- They lay eggs on land, and the incubation period is around 80 days.
- The sex of the offspring is determined by the temperature at which the eggs are incubated.
- Crocodiles are known to be caring parents, and some species protect their young.
Taxonomic Hierarchy of Crocodile
- Kingdom: Animalia – Animal, animaux, animals
- Subkingdom: Bilateria
- Infrakingdom: Deuterostomia
- Phylum: Chordata – cordés, cordado, chordates
- Subphylum: Vertebrata – vertebrado, vertébrés, vertebrates
- Infraphylum: Gnathostomata
- Superclass: Tetrapoda
- Class: Reptilia Laurenti, 1768 – répteis, reptiles, Reptiles
- Order: Crocodilia – crocodilo, jacaré, Crocodilians, crocodiles, alligators, caimans, gavials
- Family: Crocodylidae – Crocodiles
- Genus: Crocodylus Laurenti, 1768 – Crocodiles
- Species: Crocodylus porosus Schneider, 1801 – Saltwater Crocodile, Estuarine Crocodile, Saltie

List of Crocodiles of The World
Here is a list of the 23 species of crocodilians found around the world:
- American crocodile
- Chinese alligator
- Cuban crocodile
- Morelet’s crocodile
- Orinoco crocodile
- Philippine crocodile
- Siamese crocodile
- Saltwater crocodile
- Nile crocodile
- West African crocodile
- Dwarf crocodile
- New Guinea crocodile
- Freshwater crocodile
- Mugger crocodile
- Slender-snouted crocodile
- Spectacled caiman
- Yacare caiman
- Black caiman
- Broad-snouted caiman
- Smooth-fronted caiman
- Gharial
- Tomistoma
- False Gharial
Detail of Crocodiles of The World
1. American Crocodile
The American crocodile (Crocodylus acutus) is a large and powerful species that can be found throughout the Americas. They have a longer, more V-shaped snout compared to other crocodilians, which makes them more adapted to catching fish. They are a threatened species due to habitat loss and human activity, and can grow up to 6 meters in length. They are well-known for being able to live in saltwater, but you can also find them in freshwater rivers and swamps.
Habitat: American crocodiles (Crocodylus acutus) are found in parts of North, Central, and South America, typically in freshwater and brackish habitats such as rivers, swamps, and lagoons.
Description: American crocodiles have a long, narrow snout and a grayish-green coloration. They can grow up to 5 meters in length.
Teeth: American crocodiles have between 64 and 68 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: American crocodiles are considered to be a vulnerable species due to habitat loss and hunting. They are also known for being relatively docile compared to other crocodile species.

2. Saltwater Crocodile
The saltwater crocodile (Crocodylus porosus) is the largest living crocodile species in the world, and can be found in the Indo-Pacific region, from India to northern Australia. They are extremely aggressive and are known to attack humans, making them one of the most dangerous crocodiles in the world. They are able to survive in both saltwater and freshwater environments, and can grow up to 6 meters in length. Due to habitat loss and hunting, saltwater crocodiles are also considered a threatened species.
Habitat: Saltwater crocodiles (Crocodylus porosus) are found in parts of Southeast Asia and Australia, typically in brackish and saltwater habitats such as rivers, estuaries, and coastlines.
Description: Saltwater crocodiles have a broad snout and a grayish-green coloration. They are the largest crocodile species, with males growing up to 6 meters in length.
Teeth: Saltwater crocodiles have between 64 and 68 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Saltwater crocodiles are considered to be a dangerous species due to their size and aggressive nature. They are also known for being able to swim long distances in the ocean.

3. Nile Crocodile
The Nile crocodile (Crocodylus niloticus) is a large, freshwater species that can be found throughout Africa. They are one of the largest predators in Africa and can grow up to 6 meters in length. They are known for their aggressive behavior, and are responsible for numerous human deaths each year. Despite their fearsome reputation, they are also important to the ecosystems they inhabit, helping to regulate populations of prey species. Nile crocodiles are also subject to habitat loss and hunting, and are considered a threatened species.
Habitat: Nile crocodiles (Crocodylus niloticus) are found in parts of Africa, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers, swamps, and lakes.
Description: Nile crocodiles have a broad snout and a grayish-green coloration. They are one of the largest crocodile species, with males growing up to 5 meters in length.
Teeth: Nile crocodiles have between 60 and 70 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Nile crocodiles are considered to be a dangerous species due to their size and aggressive nature. They are also known for being able to hunt and kill large prey such as hippos and buffalo.

4. Gharial
The gharial (Gavialis gangeticus) is a unique crocodilian species that is found in India and Nepal. They have a long, thin snout that is adapted for catching fish, and are one of the few crocodile species that feed almost exclusively on fish. They are also distinguishable by the bulbous growth on the tip of their snout, called a “ghara.” Gharials are critically endangered due to habitat loss and hunting, and there are thought to be fewer than 250 mature individuals left in the wild.
Habitat: Gharials (Gavialis gangeticus) are found in parts of India and Nepal, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers and lakes.
Description: Gharials have a long, narrow snout and a grayish-brown coloration with white markings on their body. They can grow up to 6 meters in length.
Teeth: Gharials have between 110 and 120 teeth that are designed for catching fish.
Facts: Gharials are considered to be a critically endangered species due to habitat loss and hunting. They are also known for being the only crocodile species that exclusively eats fish.

5. Philippine Crocodile
The Philippine crocodile (Crocodylus mindorensis) is a freshwater crocodile species that is found only in the Philippines. They are a small species that can only grow to be 3 meters long. Their short, wide snout is what makes them stand out. They are also a species that is critically endangered, with less than 200 adults left in the wild. The biggest threats to the species are the loss of habitat and hunting, but there have been successful conservation efforts to protect the remaining individuals and their habitat.
Habitat: Philippine crocodiles (Crocodylus mindorensis) are found only in the Philippines, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers, swamps, and lakes.
Description: Philippine crocodiles have a broad snout and a dark green or brown coloration. They are a relatively small crocodile species, typically growing up to 3 meters in length.
Teeth: Philippine crocodiles have between 66 and 68 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Philippine crocodiles are considered to be a critically endangered species due to habitat loss and hunting. They are also culturally significant to local communities in the Philippines.

6. Cuban Crocodile
The Cuban crocodile (Crocodylus rhombifer) is a medium-sized crocodile species that is endemic to Cuba. They have a more robust body and shorter snout compared to other crocodile species, which makes them well-suited for catching a variety of prey. Cuban crocodiles are an endangered species due to habitat loss, hunting, and hybridization with the American crocodile. They are also notable for their aggressive behavior, and have been known to actively hunt in packs to take down larger prey.
Habitat: Cuban crocodiles (Crocodylus rhombifer) are found only in Cuba, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers and swamps.
Description: Cuban crocodiles have a broad snout and a green or brown coloration with yellow markings on their body. They can grow up to 3 meters in length.
Teeth: Cuban crocodiles have between 66 and 76 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Cuban crocodiles are known for being one of the most aggressive crocodile species. They are also considered to be a critically endangered species due to habitat loss and hunting.

7. Chinese Alligator
The Chinese alligator (Alligator sinensis) is a small and critically endangered crocodilian species that is endemic to China. They have a rounded snout and are the only alligator species found outside of the Americas. Chinese alligators are among the rarest reptiles in the world, with fewer than 150 individuals remaining in the wild. Habitat loss and degradation, as well as illegal poaching, have been major factors in their decline.
Habitat: Chinese alligators (Alligator sinensis) are found in parts of China, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers and wetlands.
Description: Chinese alligators have a broad snout and a dark green or brown coloration. They are one of the smallest crocodile species, typically growing up to 2 meters in length.
Teeth: Chinese alligators have between 68 and 72 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Chinese alligators are considered to be a critically endangered species due to habitat loss and hunting. They are also culturally significant in China, where they are believed to bring good luck and fortune.

8. Siamese Crocodile
The Siamese crocodile (Crocodylus siamensis) is a critically endangered crocodile species that is native to Southeast Asia. They are a relatively small species, growing up to 3 meters in length, and have a narrow snout that is well-suited for catching fish. Siamese crocodiles were once widespread throughout the region, but have been pushed to the brink of extinction due to habitat loss, hunting, and hybridization with other crocodile species. Recent conservation efforts have focused on protecting remaining populations and reintroducing captive-bred individuals into the wild.
Habitat: Siamese crocodiles (Crocodylus siamensis) are found in parts of Southeast Asia, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers, swamps, and lakes.
Description: Siamese crocodiles have a narrow snout and a dark brown or green coloration. They are a relatively small crocodile species, typically growing up to 3 meters in length.
Teeth: Siamese crocodiles have between 60 and 64 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Siamese crocodiles are considered to be a critically endangered species due to habitat loss and hunting. They are also culturally significant to local communities in Southeast Asia.

9. Orinoco Crocodile
The Orinoco crocodile (Crocodylus intermedius) is a large crocodile species that is found in South America. They have a broad, rounded snout that is well-suited for catching a variety of prey. Orinoco crocodiles are critically endangered due to habitat loss, hunting, and competition with other crocodile species. Despite their protected status, they are still threatened by poaching and other forms of illegal activity. Conservation efforts have focused on protecting their habitat, as well as promoting sustainable use of natural resources by local communities.
Habitat: Orinoco crocodiles (Crocodylus intermedius) are found in parts of South America, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers and swamps.
Description: Orinoco crocodiles have a broad snout and a dark gray or greenish coloration. They can grow up to 5 meters in length.
Teeth: Orinoco crocodiles have between 66 and 68 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Orinoco crocodiles are considered to be a critically endangered species due to habitat loss and hunting. They are also culturally significant to local communities in South America.

10. False Gharial
The false gharial (Tomistoma schlegelii) is a relatively unknown crocodile species that is found in Southeast Asia. They have a long, narrow snout that is well-adapted for catching fish, and are often mistaken for gharials due to their similar appearance. False gharials are considered a vulnerable species due to habitat loss, hunting, and pollution. They are also notable for their unique social behavior, with males engaging in vocalizations and head-slapping displays during courtship rituals. Despite being relatively unknown, conservation efforts are underway to protect remaining populations of this fascinating species.
Habitat: False gharials (Tomistoma schlegelii) are found in parts of Southeast Asia, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers and lakes.
Description: False gharials have a long, narrow snout and a dark green or brown coloration with white markings on their body. They can grow up to 5 meters in length.
Teeth: False gharials have between 72 and 76 teeth that are designed for catching fish and small prey.
Facts: False gharials are considered to be a vulnerable species due to habitat loss and hunting. They are also known for being able to swim long distances in the river.

11. Morelet’s Crocodile
Habitat: Morelet’s crocodiles (Crocodylus moreletii) are found in parts of Mexico, Belize, and Guatemala, typically in freshwater habitats such as swamps, marshes, and slow-moving rivers.
Description: Morelet’s crocodiles have a broad snout and a relatively short and stocky build. They typically grow to between 2 and 3 meters in length and have a dark green coloration with dark spots and stripes.
Teeth: Morelet’s crocodiles have 66 to 68 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Morelet’s crocodiles are named after French naturalist Pierre Marie Arthur Morelet. They are listed as a threatened species due to habitat loss and hunting, but some populations have rebounded in recent years.

12. West African Crocodile
Habitat: West African crocodiles (Crocodylus suchus) are found in parts of West and Central Africa, typically in freshwater habitats such as lakes, rivers, and swamps.
Description: West African crocodiles have a relatively narrow snout and a pale brown or grayish coloration. They typically grow to between 2 and 4 meters in length.
Teeth: West African crocodiles have between 64 and 68 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: West African crocodiles are the most widespread crocodile species in Africa. They are considered a vulnerable species due to habitat loss and hunting.

13. Dwarf Crocodile
Habitat: Dwarf crocodiles (Osteolaemus tetraspis) are found in parts of Central and West Africa, typically in freshwater habitats such as swamps and marshes.
Description: Dwarf crocodiles have a narrow snout and a brown or green coloration with black spots. They are the smallest crocodile species, typically growing to between 1.5 and 1.9 meters in length.
Teeth: Dwarf crocodiles have between 40 and 44 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Dwarf crocodiles are one of the few crocodile species that are active during the day. They are listed as a vulnerable species due to habitat loss and hunting.

14. New Guinea Crocodile
Habitat: New Guinea crocodiles (Crocodylus novaeguineae) are found in parts of New Guinea, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers and swamps.
Description: New Guinea crocodiles have a broad snout and a dark brown or greenish coloration with black spots. They typically grow to between 2 and 3 meters in length.
Teeth: New Guinea crocodiles have between 64 and 68 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: New Guinea crocodiles are considered a vulnerable species due to habitat loss and hunting. They are also an important cultural symbol in many local communities.

15. Freshwater Crocodile
Habitat: Freshwater crocodiles (Crocodylus johnsoni) are found in parts of Australia, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers and billabongs.
Description: Freshwater crocodiles have a narrow snout and a grayish coloration with dark stripes. They typically grow to between 2 and 3 meters in length.
Teeth: Freshwater crocodiles have between 66 and 70 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Freshwater crocodiles are a relatively small and shy species compared to other crocodiles. They are also a protected species in Australia and are not considered to be dangerous to humans.

16. Mugger Crocodile
Habitat: Mugger crocodiles (Crocodylus palustris) are found in parts of India, Pakistan, and Iran, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers and lakes.
Description: Mugger crocodiles have a broad snout and a light brown or gray coloration. They typically grow to between 2 and 3 meters in length.
Teeth: Mugger crocodiles have between 28 and 31 teeth in their upper jaw and 25 to 28 teeth in their lower jaw, which are designed for grabbing and crushing prey.
Facts: Mugger crocodiles are one of the few crocodile species that have been known to hunt and kill humans. They are also considered to be an important symbol in Hindu mythology.

17. Slender-Snouted Crocodile
Habitat: Slender-snouted crocodiles (Mecistops cataphractus) are found in parts of West and Central Africa, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers and swamps.
Description: Slender-snouted crocodiles have a long, slender snout and a brown or greenish coloration. They typically grow to between 2 and 3 meters in length.
Teeth: Slender-snouted crocodiles have between 68 and 72 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Slender-snouted crocodiles are one of the least-known crocodile species due to their elusive nature. They are also considered to be a vulnerable species due to habitat loss and hunting.

18. Spectacled Caiman
Habitat: Spectacled caimans (Caiman crocodilus) are found throughout Central and South America, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers and swamps.
Description: Spectacled caimans have a broad snout and a brown or greenish coloration with black stripes around their eyes. They typically grow to between 2 and 2.5 meters in length.
Teeth: Spectacled caimans have between 66 and 72 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Spectacled caimans are the most common crocodilian species in South America. They are also an important prey species for many larger predators, including jaguars and anacondas.

19. Yacare Caiman
Habitat: Yacare caimans (Caiman yacare) are found in parts of South America, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers and wetlands.
Description: Yacare caimans have a broad snout and a dark brown or grayish coloration with light markings around their eyes. They typically grow to between 2 and 3 meters in length.
Teeth: Yacare caimans have between 66 and 72 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Yacare caimans are an important species for local communities in South America, both as a source of food and for their valuable hides. They are also considered to be a low-risk species in terms of conservation status.

20. Black Caiman
Habitat: Black caimans (Melanosuchus niger) are found in parts of South America, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers and swamps.
Description: Black caimans have a broad snout and a dark brown or black coloration. They are one of the largest crocodile species in the world, typically growing to between 4 and 5 meters in length.
Teeth: Black caimans have between 66 and 72 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Black caimans are one of the apex predators in their habitat and are known to hunt a wide range of prey, including fish, birds, and even large mammals. They are also considered a vulnerable species due to habitat loss and hunting.

21. Broad-Snouted Caiman
Habitat: Broad-snouted caimans (Caiman latirostris) are found in parts of South America, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers and wetlands.
Description: Broad-snouted caimans have a broad snout and a brown or greenish coloration. They typically grow to between 2 and 3 meters in length.
Teeth: Broad-snouted caimans have between 66 and 72 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Broad-snouted caimans are an important predator in their habitat and help to regulate the population of their prey species. They are also an important source of food and income for local communities.

22. Smooth-Fronted Caiman
Habitat: Smooth-fronted caimans (Paleosuchus trigonatus) are found in parts of South America, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers and swamps.
Description: Smooth-fronted caimans have a broad snout and a dark brown or greenish coloration. They are one of the smallest caiman species, typically growing to between 1 and 1.5 meters in length.
Teeth: Smooth-fronted caimans have between 66 and 72 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Smooth-fronted caimans are one of the least-known caiman species due to their elusive nature. They are also considered to be a low-risk species in terms of conservation status.

23. Tomistoma
Habitat: Tomistomas (Tomistoma schlegelii) are found in parts of Southeast Asia, typically in freshwater habitats such as rivers and swamps.
Description: Tomistomas have a long, narrow snout and a gray or brown coloration with dark markings on their body. They typically grow to between 3 and 4 meters in length.
Teeth: Tomistomas have between 66 and 76 teeth that are designed for grabbing and holding onto prey.
Facts: Tomistomas are one of the least-known crocodile species due to their elusive nature. They are also considered to be a vulnerable species due to habitat loss and hunting.

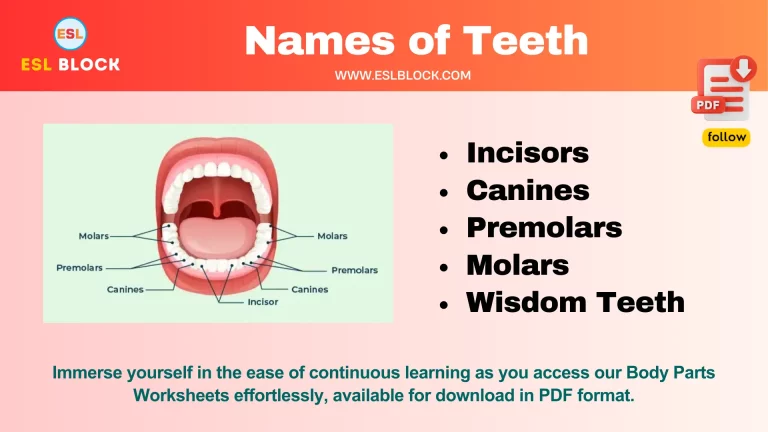
Crocodiles of The World Charts | Printable
Crocodiles of the World charts are printable resources that provide valuable information about the different species of crocodiles found around the globe. These charts are a great way for students, teachers, and nature lovers to learn more about crocodiles’ unique characteristics and where they live.
By using these charts, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the diversity of crocodile species, their geographical distribution, and their importance to the ecosystem. These charts are also useful for conservationists and researchers who want to track the population of different crocodile species and identify threats to their survival.
Overall, the Crocodiles of the World charts are a great resource for anyone interested in learning more about these remarkable creatures.




Conclusion
In conclusion, crocodiles are a diverse group of reptiles found in a variety of habitats around the world. They are fascinating creatures that have been around for millions of years and have adapted to a wide range of environmental conditions.
While they are often portrayed as dangerous and aggressive predators, crocodiles play an important role in their ecosystems, and their presence is an indicator of a healthy ecosystem.
Unfortunately, many species of crocodiles are threatened by habitat loss, poaching, and climate change. Conservation efforts are crucial to ensuring the survival of these iconic and ancient reptiles for future generations to appreciate and enjoy.
If you have enjoyed “crocodiles of the world, “I would be very thankful if you’d help spread it by emailing it to your friends or sharing it on Twitter, Instagram, Pinterest, or Facebook. Thank you!
With ESLBLOCK, you will study with new ideas. If you doubt the qualities of the crocodiles of the world, reach us through our blog’s comment section. Keep checking back! We’ll do our best to give you feedback as soon as possible. Thank you!
Also Read: Sentence Structures Worksheets
Recap of what we just learned
- Crocodiles of The World
- How did crocodiles get their name?
- General Features of Crocodiles of the World
- Taxonomic Hierarchy of Crocodile
- List of Crocodiles of The World
- Detail of Crocodiles of The World
- Crocodiles of The World Charts | Printable
Related Articles
Here are some more lists for you!
- List of Fish: Types of Fish with Interesting Facts and Pictures
- List of Mollusks | Types of Mollusks with Interesting Facts
- List Of Farm Animals: Different Types of Farm Animals
- Shellfish | List of Shellfish with Interesting Facts
- List of Crustaceans: Cool Facts with Pictures


Awesome
How do you get the charts
I have made this chart!