Parts of Brain: A Comprehensive Brain Vocabulary
Understanding the parts of the brain and their functions is essential for appreciating how this complex organ controls every aspect of our lives.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore key terms and vocabulary related to the brain’s anatomy, helping you gain a deeper insight into how it processes information, regulates bodily functions, and influences behavior.
Whether you’re a student, educator, or simply curious about neuroscience, this article will provide the foundational knowledge needed to understand the brain’s intricate workings.
“Verified for accuracy, parts of the brain vocabulary listed here have been sourced from reputable references. Source: Your Info Master.”
- Parts of the Brain
- Brain Glossary
- Acetylcholine
- Action Potential
- Amygdala
- Axon
- Basal Ganglia
- Blood-Brain Barrier
- Brainstem
- Cerebellum
- Cerebral Cortex
- Cerebrospinal Fluid
- Corpus Callosum
- Dendrites
- Dopamine
- EEG (Electroencephalogram)
- Frontal Lobe
- Glial Cells
- Hippocampus
- Hypothalamus
- Limbic System
- Medulla Oblongata
- Myelin Sheath
- Neuroplasticity
- Neurotransmitters
- Occipital Lobe
- Parietal Lobe
- Pituitary Gland
- Pons
- Serotonin
- Synapse
- Temporal Lobe
- Thalamus
- Ventricles
- How does the brain work?
- Conclusion
- Related Articles
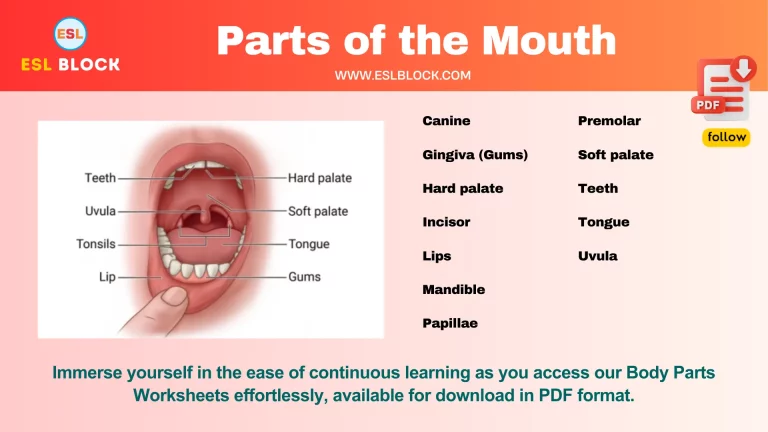
Read also: Parts of the Face with Pictures
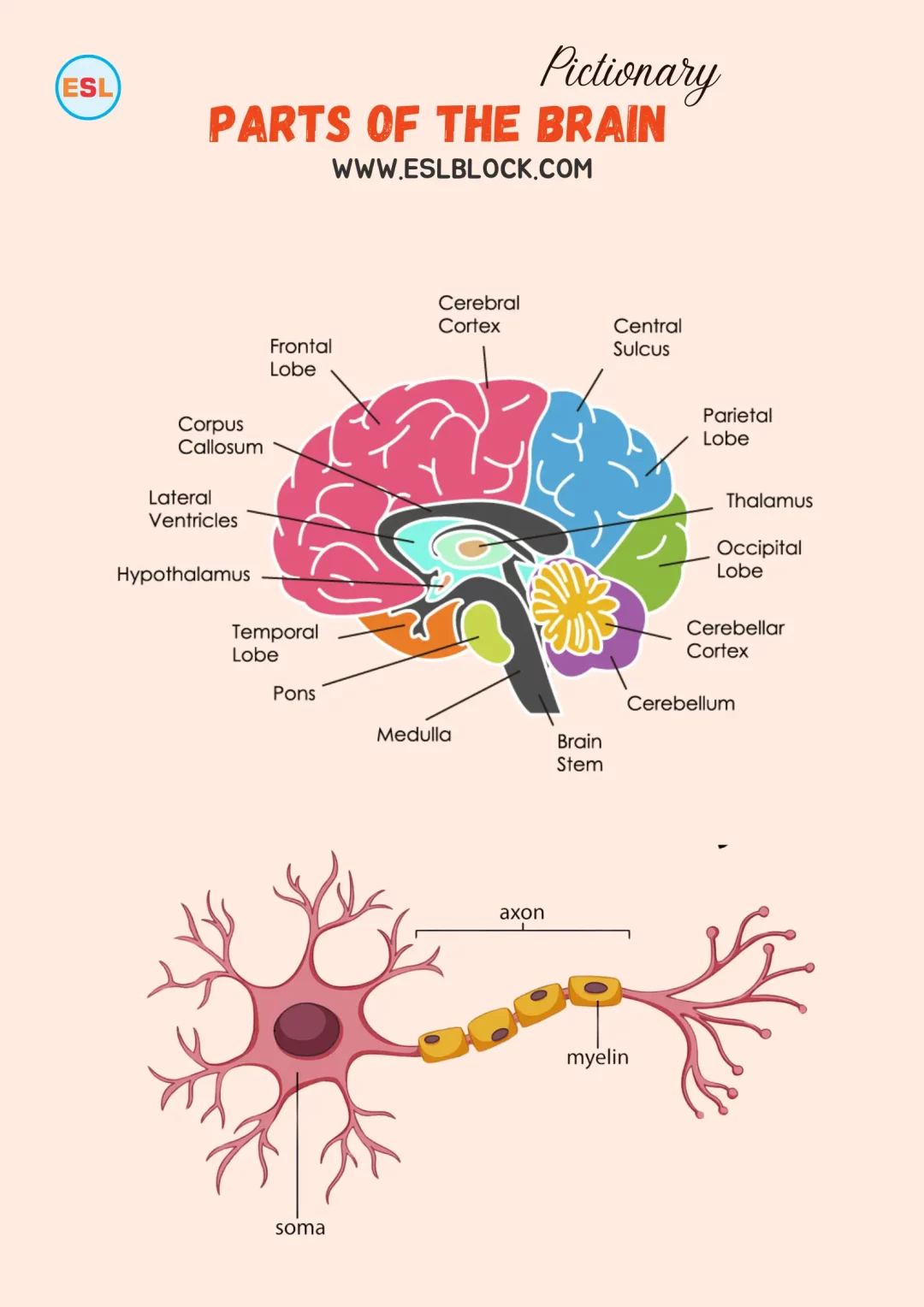
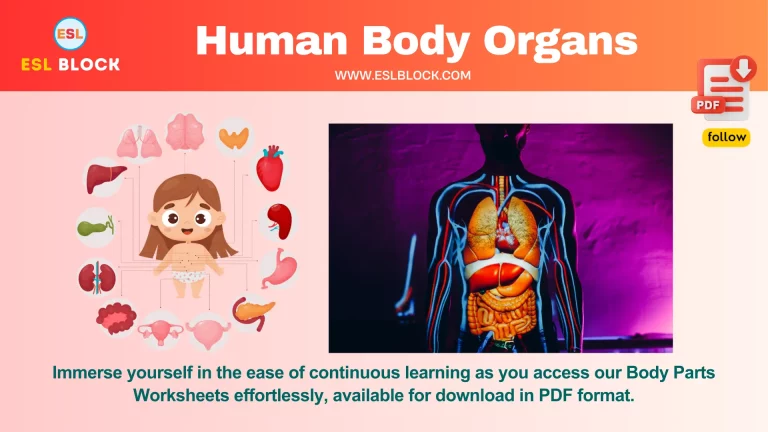
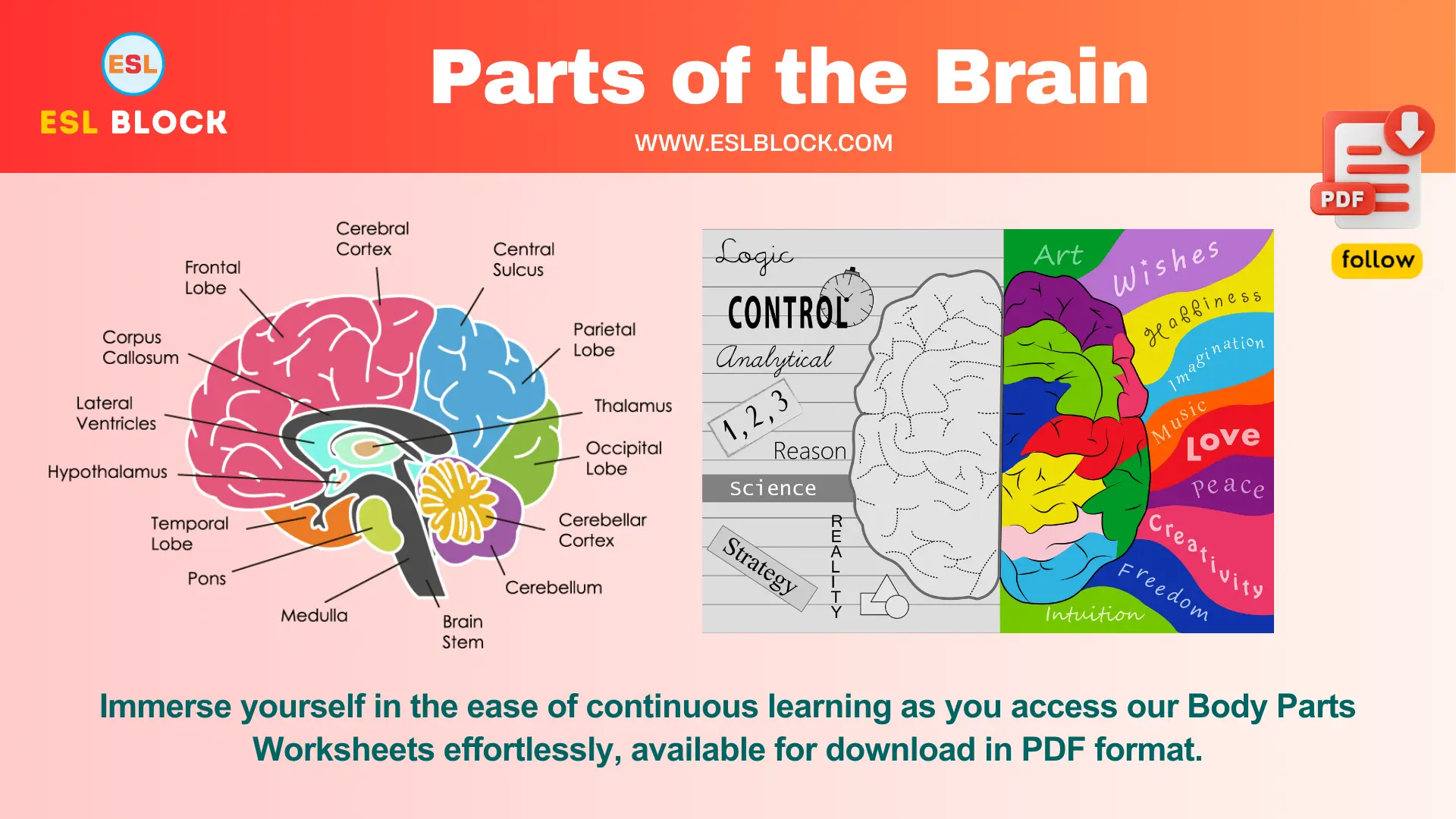
Parts of the Brain
Cerebrum
The largest part of the brain is responsible for voluntary activities, sensory perception, and complex cognitive functions like thinking, learning, and memory.
Cerebellum
Located at the back of the brain, it coordinates voluntary movements, balance, and posture.
Brainstem
Connects the brain to the spinal cord and controls basic life functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure.
Frontal Lobe
Involved in decision-making, problem-solving, planning, and controlling behavior and emotions.
Parietal Lobe
It processes sensory information such as touch, temperature, and pain and helps with spatial orientation and body awareness.
Temporal Lobe
Responsible for processing auditory information, memory, and language comprehension.
Occipital Lobe
The main center for visual processing is interpreting visual information from the eyes.
Thalamus
Acts as a relay station for sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex and regulates consciousness, sleep, and alertness.
Hypothalamus
Regulates vital bodily functions such as hunger, thirst, sleep, body temperature, and hormone secretion.
Hippocampus
It is essential for forming new memories and is associated with learning and emotions.
Amygdala
Involvement in emotion processing, particularly fear and pleasure responses, helps form emotional memories.
Corpus Callosum
A bundle of nerve fibers connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain, facilitating communication between them.
Pituitary Gland
Often referred to as the “master gland,” it controls various hormonal functions by releasing hormones into the bloodstream.
Medulla Oblongata
Part of the brainstem that regulates autonomic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion.
Pons
It is part of the brainstem that relays signals between the cerebrum and cerebellum and helps regulate sleep and breathing.
Basal Ganglia
A group of structures coordinates movement and behavior and regulates voluntary motor control and procedural learning.
Limbic System
It is a complex system within the brain that includes the hippocampus, amygdala, and other structures; it is involved in emotion, behavior, and long-term memory.
Midbrain
It is part of the brainstem that controls eye movements, auditory processing, and motor control.
Also Check: 25 Chili Pepper Types
Brain Glossary
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter involved in learning, memory, and muscle contraction.
Action Potential
A rapid rise and fall in electrical potential across a neuron’s membrane enables the transmission of nerve impulses.
Amygdala
A brain region involved in emotion processing, particularly fear and pleasure responses, and forming emotional memories.
Axon
The long, slender projection of a neuron that transmits electrical impulses away from the neuron’s cell body.
Basal Ganglia
A group of structures involved in coordinating movement, behavior, and voluntary motor control.
Blood-Brain Barrier
A selective barrier that protects the brain from harmful substances in the bloodstream while allowing essential nutrients to pass through.
Brainstem
The part of the brain that connects to the spinal cord and controls basic life functions such as breathing, heartbeat, and blood pressure.
Cerebellum
The region at the back of the brain is responsible for coordinating voluntary movements, balance, and posture.
Cerebral Cortex
The cerebrum’s outer layer is involved in higher brain functions such as thought, perception, and decision-making.
Cerebrospinal Fluid
A clear fluid that surrounds and protects the brain and spinal cord, providing cushioning and nutrient transport.
Corpus Callosum
A bundle of nerve fibers connects the left and right hemispheres of the brain, facilitating communication between them.
Dendrites
The branched extensions of a neuron that receive signals from other neurons and transmit them to the cell body.
Dopamine
A neurotransmitter regulates reward, motivation, movement, and emotional responses.
EEG (Electroencephalogram)
A test that measures electrical activity in the brain using electrodes placed on the scalp.
Frontal Lobe
The part of the brain involved in decision-making, problem-solving, planning, and controlling behavior and emotions.
Glial Cells
Non-neuronal cells in the brain provide support and protection for neurons and maintain homeostasis.
Hippocampus
A brain structure is essential for the formation of new memories and is associated with learning and emotions.
Hypothalamus
A region of the brain that regulates vital bodily functions such as hunger, thirst, sleep, body temperature, and hormone secretion.
Limbic System
A complex system within the brain that includes structures such as the hippocampus and amygdala is involved in emotion, behavior, and long-term memory.
Medulla Oblongata
Part of the brainstem that regulates autonomic functions such as breathing, heart rate, and digestion.
Myelin Sheath
A fatty layer that covers and insulates axons, speeding up the transmission of electrical impulses along nerve cells.
Neuroplasticity
The brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers transmit signals across synapses from one neuron to another.
Occipital Lobe
The brain region is responsible for the visual processing and interpretation of visual information from the eyes.
Parietal Lobe
The part of the brain that processes sensory information such as touch, temperature, and pain and helps with spatial orientation and body awareness.
Pituitary Gland
Often referred to as the “master gland,” it controls various hormonal functions by releasing hormones into the bloodstream.
Pons
It is part of the brainstem that relays signals between the cerebrum and cerebellum and helps regulate sleep and breathing.
Serotonin
A neurotransmitter that affects mood, appetite, and sleep and plays a role in feelings of well-being and happiness.
Synapse
The junction between two neurons is where neurotransmitters are released to transmit signals.
Temporal Lobe
The brain region is responsible for processing auditory information, memory, and language comprehension.
Thalamus
A relay station for sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex, regulating consciousness, sleep, and alertness.
Ventricles
Cavities within the brain that produce and contain cerebrospinal fluid provide cushioning and nutrient transport.
How does the brain work?
The brain sends and receives chemical and electrical signals throughout the body. Different signals control different processes, and your brain interprets each. Some make you feel tired, for example, while others make you feel pain.
Some messages are kept within the brain, while others are relayed through the spine and across the body’s vast network of nerves to distant extremities. To do this, the central nervous system relies on billions of neurons (nerve cells).
Chemical and Electrical Signals
The brain uses neurotransmitters to send chemical messages between neurons. These chemicals either excite or inhibit neuronal activity, influencing various functions like mood, arousal, and cognition. Electrical signals, or action potentials, travel along neurons’ axons, allowing rapid communication within the nervous system.
Neurons and Synapses
Neurons are the building blocks of the brain and nervous system. Each neuron consists of a cell body, dendrites, and an axon. Dendrites receive signals from other neurons, while the axon sends signals away from the cell body. At synapses, neurons communicate with each other through the release and reception of neurotransmitters, creating a complex network of communication.
Central Nervous System
The brain and spinal cord form the central nervous system (CNS), which processes information and coordinates responses. The brain interprets sensory data, makes decisions, and sends instructions through the spinal cord to the peripheral nervous system, which carries out the commands.
Brain Regions and Functions
Different regions of the brain have specialized functions. The frontal lobe is involved in decision-making and problem-solving, the parietal lobe processes sensory information, the occipital lobe handles visual processing, and the temporal lobe is responsible for auditory information and memory. The brainstem controls basic life functions, while the cerebellum coordinates movement and balance.
Network of Nerves
The peripheral nervous system (PNS) extends from the CNS to the rest of the body, transmitting signals to and from the brain. Sensory nerves bring information to the brain, while motor nerves carry instructions from the brain to muscles and glands. This network enables the body to respond to internal and external stimuli, maintaining homeostasis and supporting daily activities.
Also Read: Body Parts Names
Conclusion
By familiarizing yourself with the parts of the brain and their specific functions, you can better appreciate this vital organ’s remarkable complexity and efficiency. From regulating basic bodily functions to enabling complex cognitive processes, each part of the brain plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being.
Stay informed about brain health and continue exploring the fascinating world of neuroscience to enhance your understanding and support your mental well-being.
If you have enjoyed “Parts of the Brain,” I would be very thankful if you could help spread the word by emailing it to your friends or sharing it on Twitter, Instagram, Pinterest, or Facebook. Thank you!
ESLBLOCK will teach you new things. If you have questions about the major parts of the brain, you can ask us in the comments section of our blog. Come back often! We will try to answer you quickly. Thank you!
Related Articles
Here are some more lists for you!
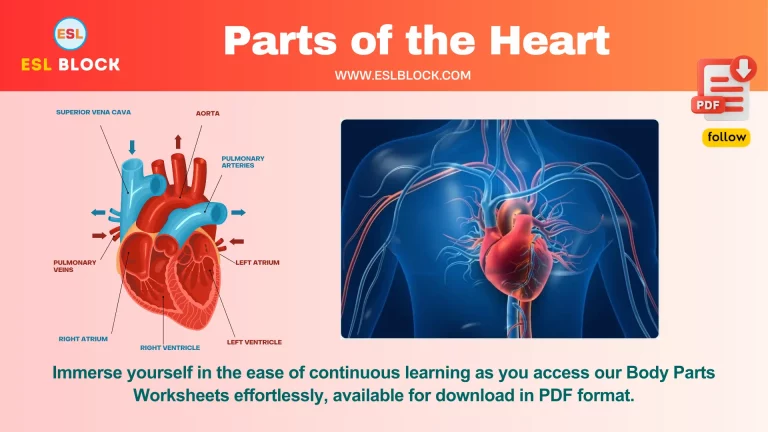
- Parts of the Heart
- Bone Names of the Human Skeleton
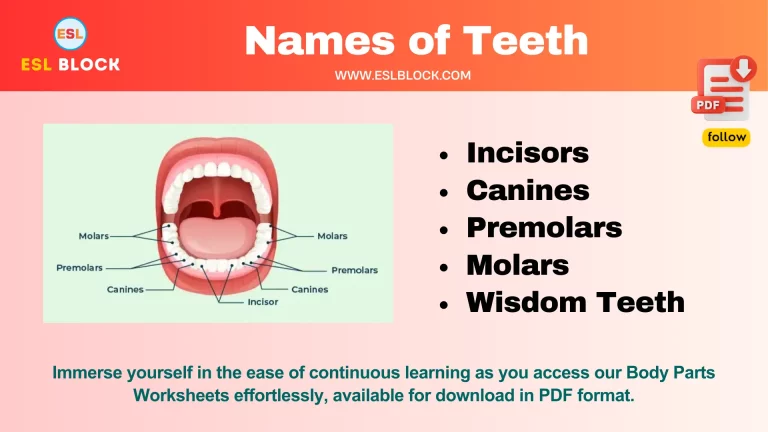
- Names of Teeth in English with Pictures
- Parts of the Mouth Vocabulary
- Parts of the Hand Vocabulary