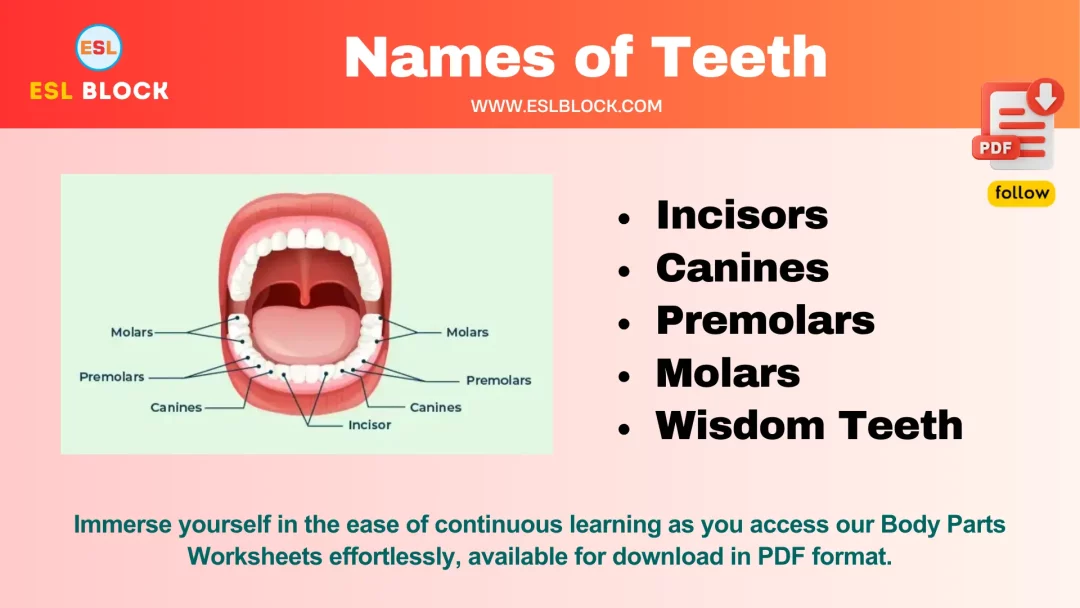
25 Chili Pepper Types With Scoville Heat

![]()
Welcome to the vibrant world of Chili Pepper Types! With an array of shapes, sizes, and flavors, peppers are the versatile fruits derived from flowering plants within the nightshade family.
Whether you crave heat, sweetness, spiciness, or mildness, peppers have it all. Remarkably, despite their diverse characteristics, every pepper falls under the biological classification Capsicum.
Found in cuisines across the globe, peppers play a starring role in dishes ranging from the piquant salsas of Mexico to the fiery green chili in Indian curry and the zest of red chili in Korean kimchi.
Join us on a flavorful journey as we delve into the fascinating realm of peppers, exploring their rich diversity and culinary significance.
Scoville Scale
Ever wondered how spicy a pepper can be? Well, there’s a scale called the Scoville scale that measures it. Bell peppers, which are not spicy at all, are rated as zero Scoville heat units. On the other hand, some of the world’s spiciest peppers can go up to three million units!
Now, let’s talk about spiciness levels. Peppers with zero to 4,000 units are considered mild, 4,000 to 15,000 is medium, 15,000 to 50,000 is hot, and anything over 50,000 is like a fire explosion in your mouth.
Most of the heat in a pepper is concentrated in the seeds and ribs. So, if you want to tone down the spiciness, just remove them when you’re using peppers in your cooking. Easy, right?
Chili Pepper List
Here is the list of Chili Pepper:
- Jalapeño (Capsicum annuum)
- Habanero (Capsicum chinense)
- Serrano (Capsicum annuum)
- Poblano (Capsicum annuum)
- Anaheim (Capsicum annuum)
- Cayenne (Capsicum annuum)
- Thai Bird’s Eye (Capsicum annuum)
- Scotch Bonnet (Capsicum chinense)
- Fresno (Capsicum annuum)
- Cherry Pepper (Capsicum annuum)
- Pasilla (Capsicum annuum)
- Chipotle (Capsicum annuum)
- Shishito (Capsicum annuum)
- Banana Pepper (Capsicum annuum)
- Peperoncini (Capsicum annuum)
- Pimiento (Capsicum annuum)
- Aji Amarillo (Capsicum baccatum)
- Ghost Pepper (Bhut Jolokia – Capsicum chinense)
- Trinidad Moruga Scorpion (Capsicum chinense)
- Paprika Pepper (Capsicum annuum)
- Piquillo (Capsicum annuum)
- Cascabel (Capsicum annuum)
- Pasilla de Oaxaca (Capsicum annuum)
- NuMex Twilight (Capsicum annuum)
- Datil (Capsicum chinense)
Chili Pepper Details
Here is the detail of each type of chili pepper:
1. Jalapeño (Capsicum annuum)
The Jalapeño Pepper, originating from Mexico, is a culinary gem known for its vibrant flavor and moderate heat. Commonly referred to as “jalapeño” in English, it is called “cuaresmeño” in Mexico.
This pepper boasts a distinctive conical shape, reaching a size of about 2 to 3 inches in length. With a Scoville Scale rating ranging from 2,500 to 8,000 heat units, jalapeños offer a mild to medium level of spiciness. They exhibit a spectrum of colors, transitioning from green to red as they mature.
Jalapeños are culinary chameleons, finding their way into an array of dishes worldwide. From salsas to nachos, their versatile flavor adds a zesty kick.
Cultivated in warm climates, these peppers thrive in well-drained soil and require full sunlight. They are typically planted in the spring and early summer, with a harvesting season extending from late summer to early fall.
Whether used fresh, pickled, or dried, jalapeños contribute a distinct heat and flavor to dishes, making them a beloved ingredient in many cuisines.

2. Habanero (Capsicum chinense)
Originating from the Amazon region and named after the Cuban city of La Habana, the Habanero pepper (Capsicum chinense) is a fiery delight renowned for its intense heat and tropical flavor.
Locally known as “Scotch Bonnet” in some regions, this small, lantern-shaped pepper typically measures 1 to 2 inches in length.
The Habanero’s flavor profile is distinctive, offering fruity and citrusy notes beneath the formidable heat. Scoring between 100,000 to 350,000 Scoville Heat Units (SHU), it ranks among the hotter peppers on the scale.
Habaneros exhibit a vibrant range of colors, transitioning from green to shades of orange, red, or even brown as they ripen. Embracing their intense heat, these peppers are integral to Caribbean, Mexican, and Central American cuisines, adding a bold kick to sauces, salsas, and marinades.
Cultivating Habaneros demands warm, tropical conditions, with well-drained soil and ample sunlight. Typically planted in the spring and early summer, they thrive in hot climates and are ready for harvest during the late summer and fall months, making them a favorite for spice enthusiasts worldwide.

3. Serrano (Capsicum annuum)
Originating from Mexico, the Serrano pepper is a vibrant, elongated variety measuring 1 to 2 inches. With a heat level ranging from 10,000 to 23,000 SHU, Serranos add a medium to hot kick to dishes.
Adaptable to various cuisines, they boast a colorful transition from green to red. Thriving in warm climates, Serranos require well-drained soil and full sunlight.
Planting typically occurs in spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall. A versatile pepper, Serrano is a popular choice for salsas, sauces, and spicy dishes.

4. Poblano (Capsicum annuum)
Hailing from Mexico, the Poblano pepper is recognized for its large, heart-shaped appearance, measuring around 4 to 6 inches. With a mild heat ranging from 1,000 to 2,000 SHU, Poblanos offer a rich flavor profile, often used in Mexican cuisine. They transition from green to dark red when fully ripe.
Cultivating well in warm climates, Poblanos thrive with full sunlight and well-drained soil. Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvest in late summer and fall.
Poblanos are versatile, used in a variety of dishes such as chiles rellenos and mole sauces.

5. Anaheim (Capsicum annuum)
Originating from the United States, the Anaheim pepper is a mild, elongated variety measuring 6 to 8 inches. With a heat level ranging from 500 to 2,500 SHU, it is often used in Southwestern and Mexican cuisines.
Anaheim peppers transition from green to red as they ripen. Thriving in warm climates, they require full sunlight and well-drained soil. Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall.
Anaheims are versatile, used in dishes like chile rellenos and salsas, adding a mild heat and vibrant flavor.

6. Cayenne (Capsicum annuum)
Known for its elongated and slender shape, the Cayenne pepper originates from French Guiana. Measuring 4 to 6 inches, Cayennes pack a spicy punch, ranging from 30,000 to 50,000 SHU.
With a bright red color, they are often dried and ground into a spice. Thriving in warm climates, Cayennes require full sunlight and well-drained soil.
Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall. Cayennes are a key ingredient in spicy dishes, hot sauces, and as a flavor enhancer in various cuisines.
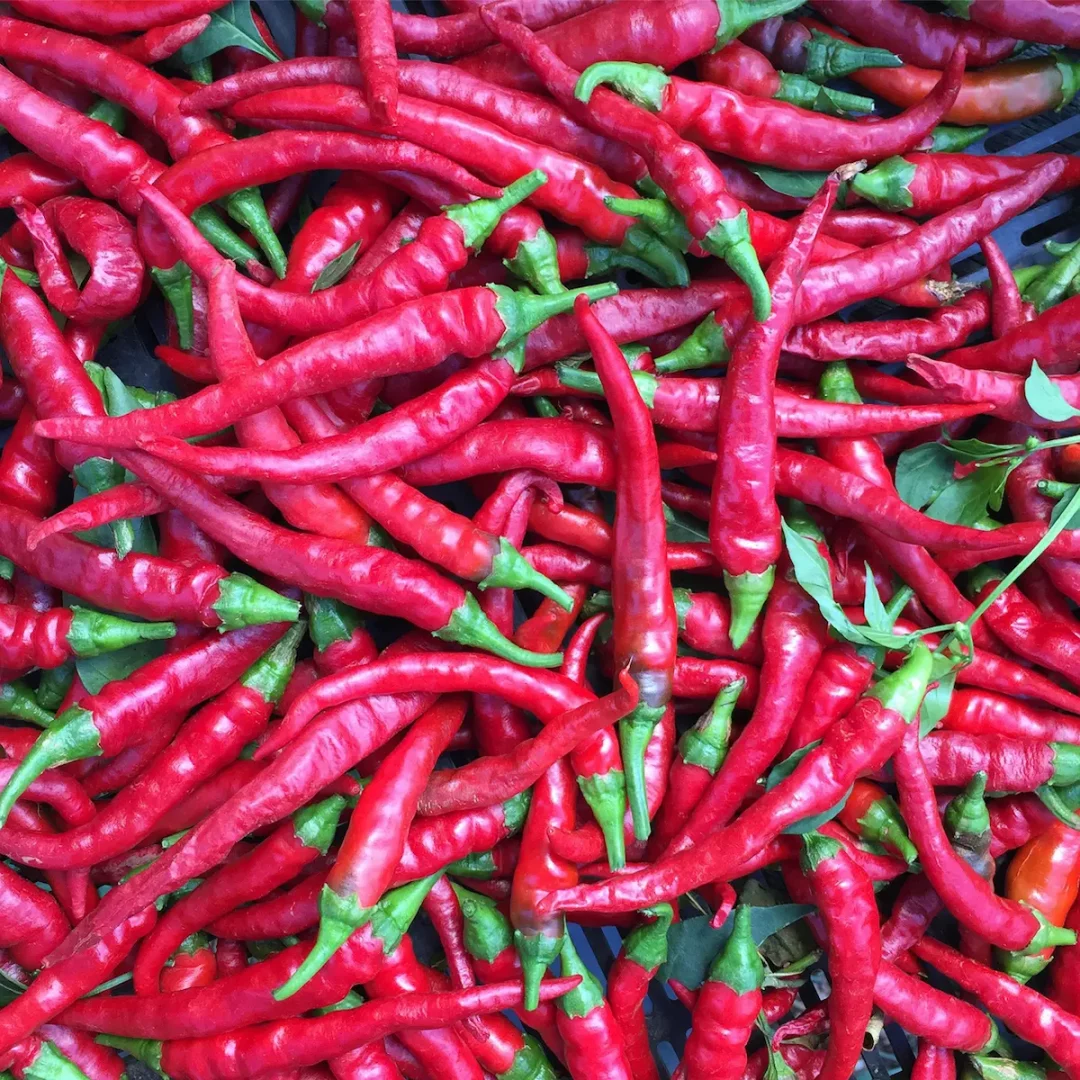

7. Thai Bird’s Eye (Capsicum annuum)
Hailing from Thailand, the Thai Bird’s Eye pepper is a small, slender variety, measuring around 1 to 2 inches. It ranks high on the heat scale, ranging from 50,000 to 100,000 SHU.
Vibrant green to red when ripe, these peppers are essential in Thai cuisine, providing intense spiciness. Thriving in warm climates, they require full sunlight and well-drained soil.
Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall. Thai Bird’s Eye peppers are used to add heat to curries, soups, and various Thai dishes.
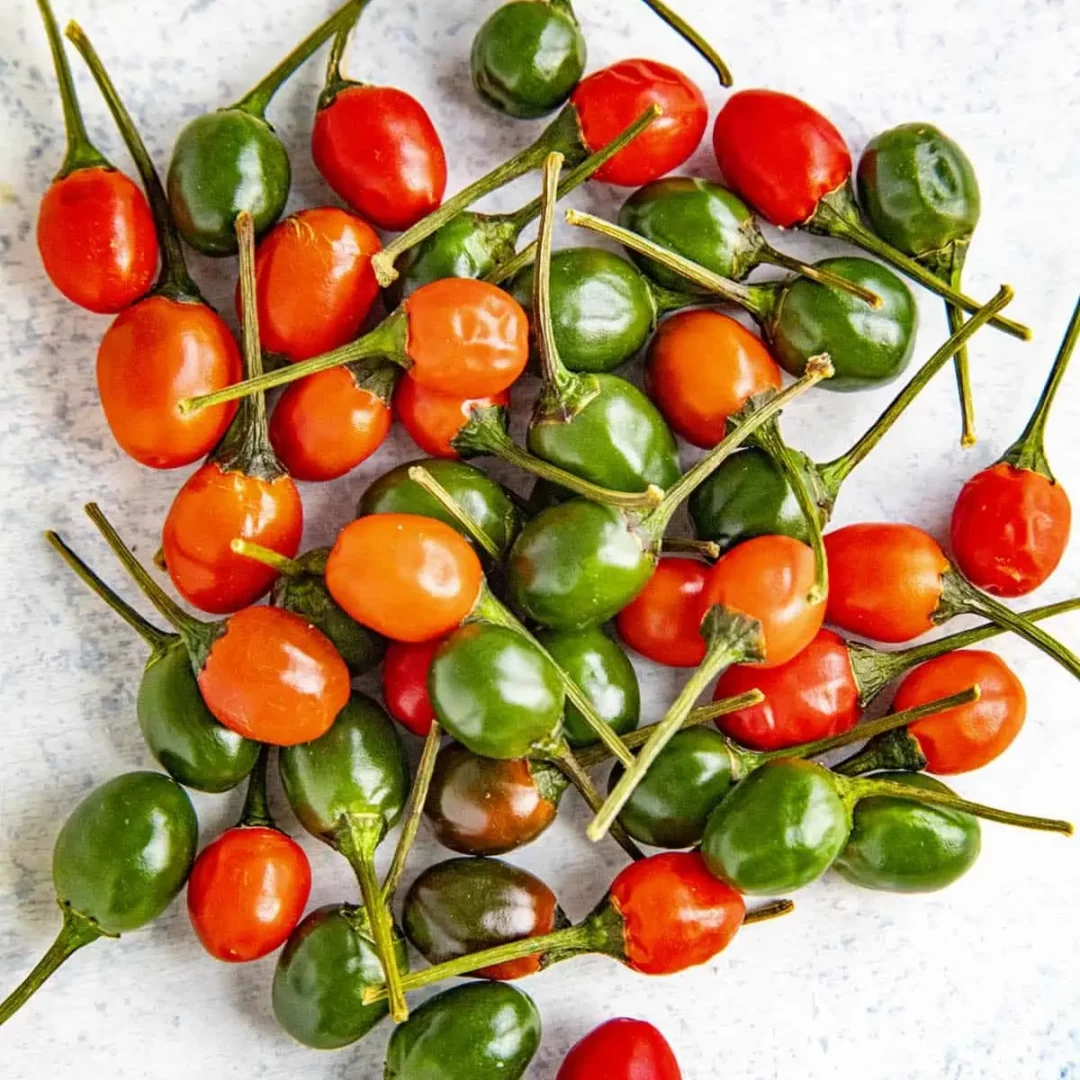

8. Scotch Bonnet (Capsicum chinense)
Also known as “Bonney peppers,” Scotch Bonnets originate from the Caribbean and are closely related to Habaneros. With a lantern-like shape and vibrant colors, they measure 1 to 2 inches. These peppers are among the spiciest, scoring between 100,000 to 350,000 SHU.
Used prominently in Caribbean cuisine, they thrive in warm, tropical conditions, requiring full sunlight and well-drained soil.
Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall. Scotch Bonnets add intense heat and tropical flavor to jerk sauces, hot pepper sauces, and other Caribbean dishes.

9. Fresno (Capsicum annuum)
The Fresno pepper, originating from the United States, is a moderately hot variety with a slender, conical shape, measuring 2 to 3 inches. Ranging from 2,500 to 10,000 SHU, Fresnos transition from green to red when fully ripe.
Adaptable to various cuisines, they thrive in warm climates, requiring full sunlight and well-drained soil. Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall.
Fresnos add a medium heat and vibrant color to dishes, making them a popular choice for salsas, hot sauces, and other spicy recipes.
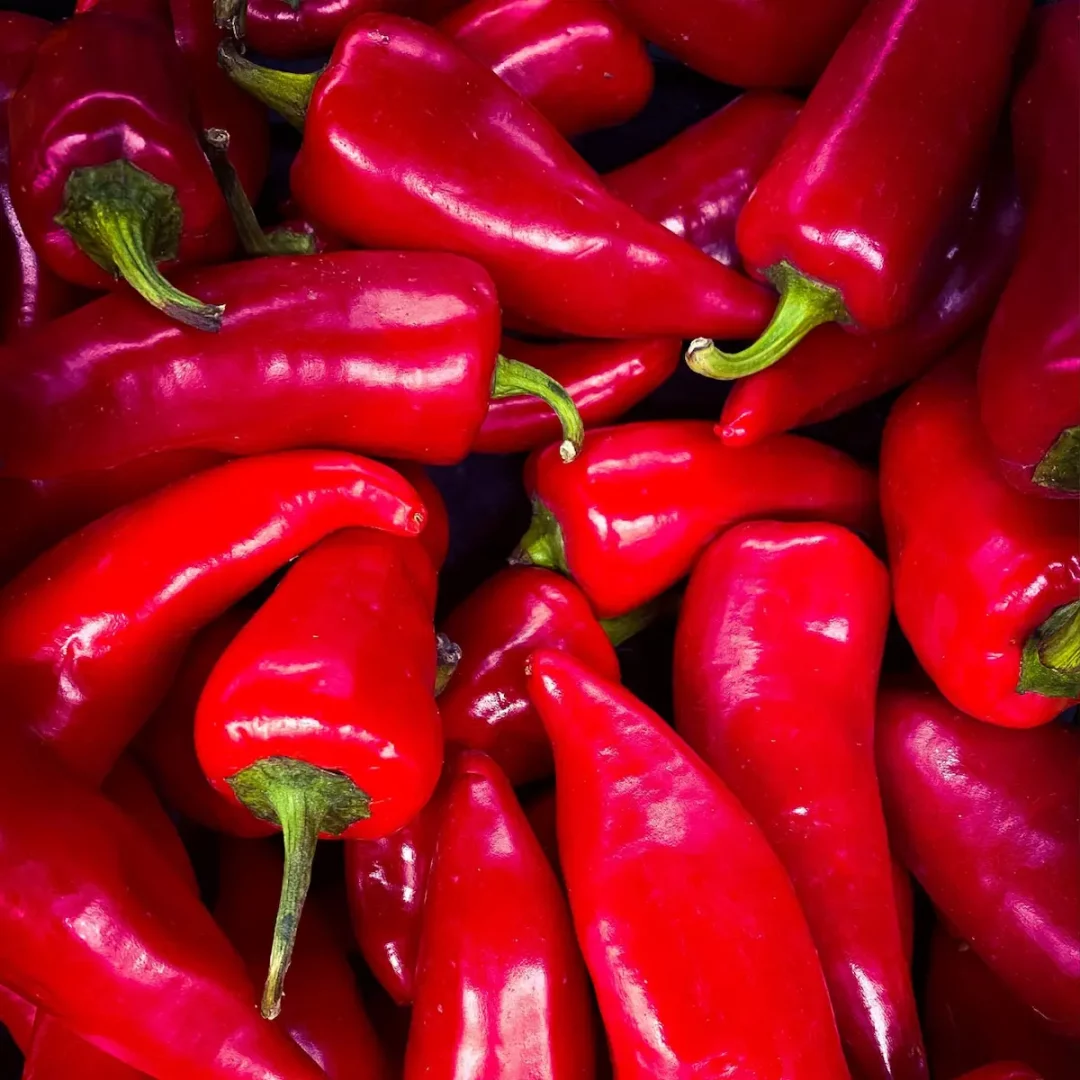

10. Cherry Pepper (Capsicum annuum)
The Cherry Pepper, originating from the United States, is a small, round pepper with a sweet and mild flavor. Measuring around 1 to 2 inches, it is often used in pickling and as a garnish. With a low heat level, ranging from 100 to 1,000 SHU, Cherry Peppers transition from green to red as they ripen.
Adaptable to various cuisines, they thrive in warm climates, requiring full sunlight and well-drained soil.
Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall. Cherry Peppers are a delightful addition to salads, antipasto platters, and pickled dishes.

11. Pasilla (Capsicum annuum)
Originating from Mexico, the Pasilla pepper is a mild to moderately hot variety, measuring around 6 to 8 inches. With a rich and earthy flavor, it is commonly used in Mexican cuisine, especially in mole sauces.
Pasillas transition from green to dark brown when fully ripe. Thriving in warm climates, they require full sunlight and well-drained soil. Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall.
Pasillas add depth and complexity to dishes, making them a key ingredient in various Mexican recipes.

12. Chipotle (Capsicum annuum)
Chipotle peppers are dried and smoked ripe Jalapeños, originating from Mexico. With a wrinkled appearance, they measure around 2 to 4 inches. Chipotles offer a unique smoky flavor and a medium heat level, ranging from 2,500 to 8,000 SHU.
Adaptable to various cuisines, they thrive in warm climates, requiring full sunlight and well-drained soil. Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall.
Chipotles are a popular ingredient in Mexican and southwestern dishes, adding a distinctive smokiness to salsas, sauces, and marinades.

13. Shishito (Capsicum annuum)
Hailing from Japan, the Shishito pepper is a small, wrinkled variety, measuring around 2 to 4 inches. Typically mild, with occasional bursts of heat, Shishitos are enjoyed for their unique flavor.
Transitioning from green to red as they ripen, they thrive in warm climates, requiring full sunlight and well-drained soil.
Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall. Shishitos are often pan-fried or grilled whole and served as a popular appetizer, bringing a delightful combination of mild spiciness and smoky flavor.

14. Banana Pepper (Capsicum annuum)
Originating from the United States, the Banana Pepper is a mild and sweet variety, known for its long, curved shape, measuring 6 to 8 inches. With a heat level ranging from 0 to 500 SHU, Banana Peppers transition from green to yellow and finally to red as they ripen.
Adaptable to various cuisines, they thrive in warm climates, requiring full sunlight and well-drained soil.
Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall. Banana Peppers are a versatile choice, used in salads, sandwiches, and pickled dishes, adding a touch of mild sweetness.
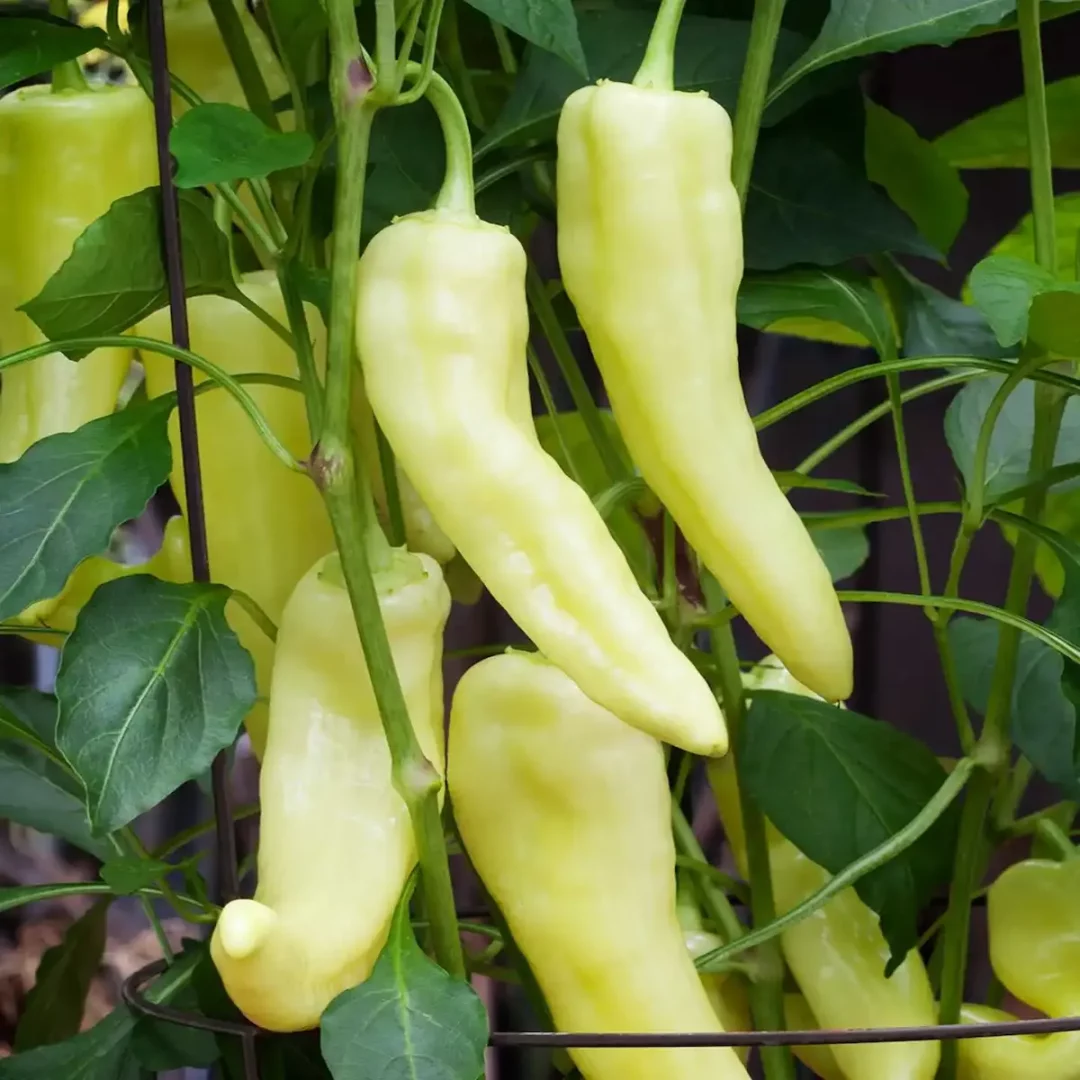

15. Peperoncini (Capsicum annuum)
Hailing from Italy, the Peperoncini is a mildly spicy pepper, measuring around 2 to 3 inches. With a heat level ranging from 100 to 500 SHU, these peppers transition from green to yellow as they ripen.
Adaptable to various cuisines, they thrive in warm climates, requiring full sunlight and well-drained soil. Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall.
Peperoncini peppers are commonly pickled and used as a condiment, adding a mild heat and tangy flavor to salads, sandwiches, and antipasto platters.

16. Pimiento (Capsicum annuum)
The Pimiento pepper, originating from Spain, is a sweet and mild variety, known for its heart-shaped appearance and vibrant red color. Measuring around 2 to 3 inches, it has a heat level ranging from 0 to 100 SHU.
Thriving in warm climates, Pimientos require full sunlight and well-drained soil. Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall. Pimientos are often used as stuffing in olives and as a key ingredient in pimento cheese, adding a burst of sweetness and color to various dishes.

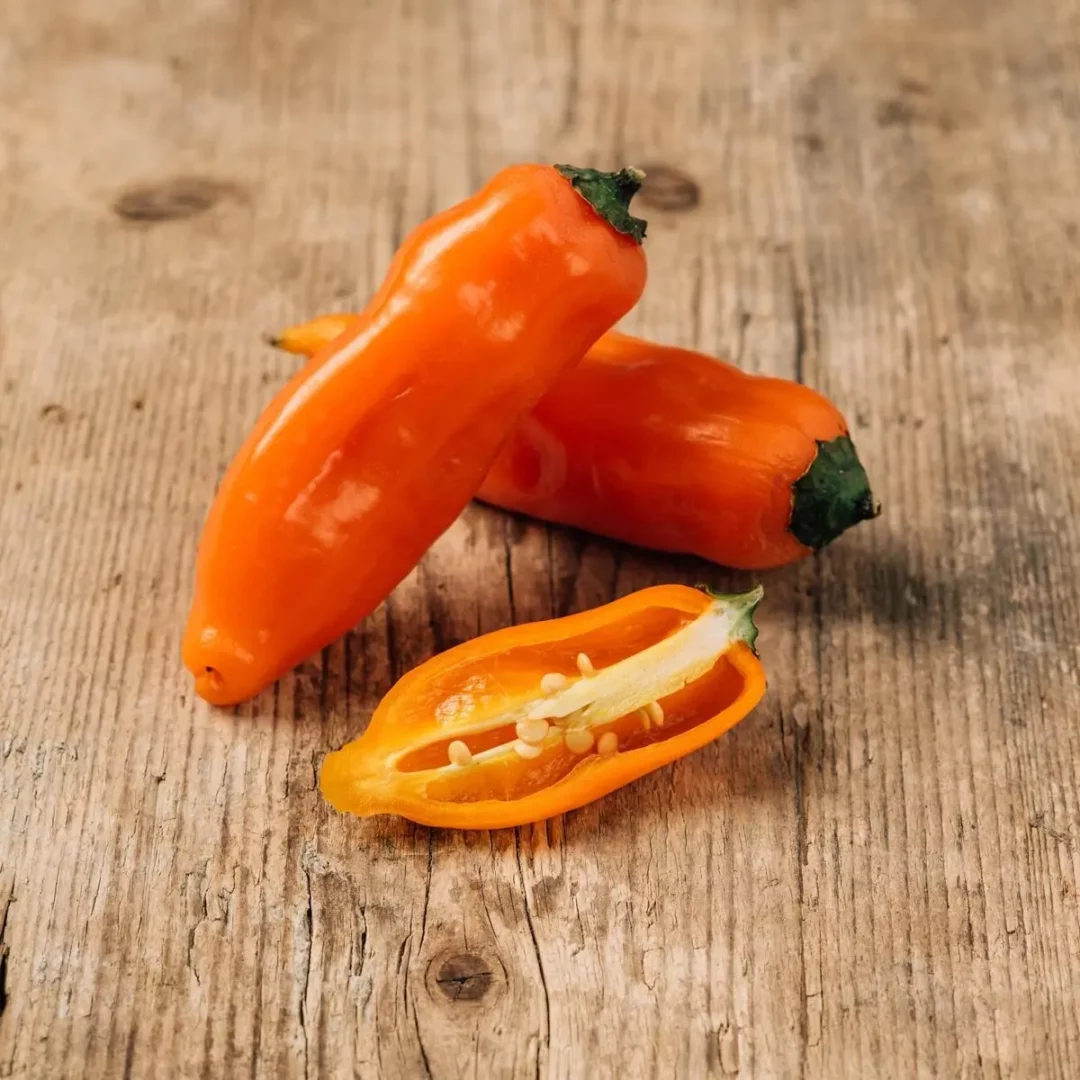
17. Aji Amarillo (Capsicum baccatum)
Originating from Peru, the Aji Amarillo is a medium to hot pepper, measuring around 4 to 5 inches. With a distinctive bright yellow color, it packs a flavorful punch, often described as fruity and citrusy.
Aji Amarillos thrive in warm climates, requiring full sunlight and well-drained soil. Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall. Essential in Peruvian cuisine, these peppers are used in various sauces, stews, and marinades, providing both heat and a unique tropical flavor.

18. Ghost Pepper (Bhut Jolokia – Capsicum chinense)
Originating from India, the Ghost Pepper, or Bhut Jolokia, is one of the world’s hottest peppers, measuring over 1 million SHU. With a wrinkled appearance and bright red color, it delivers intense heat with hints of fruity and smoky flavors.
Thriving in warm climates, Ghost Peppers require full sunlight and well-drained soil. Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall. Used sparingly in cuisines, particularly in curries and hot sauces, Ghost Peppers are known for their extreme spiciness, providing a fiery kick to dishes.
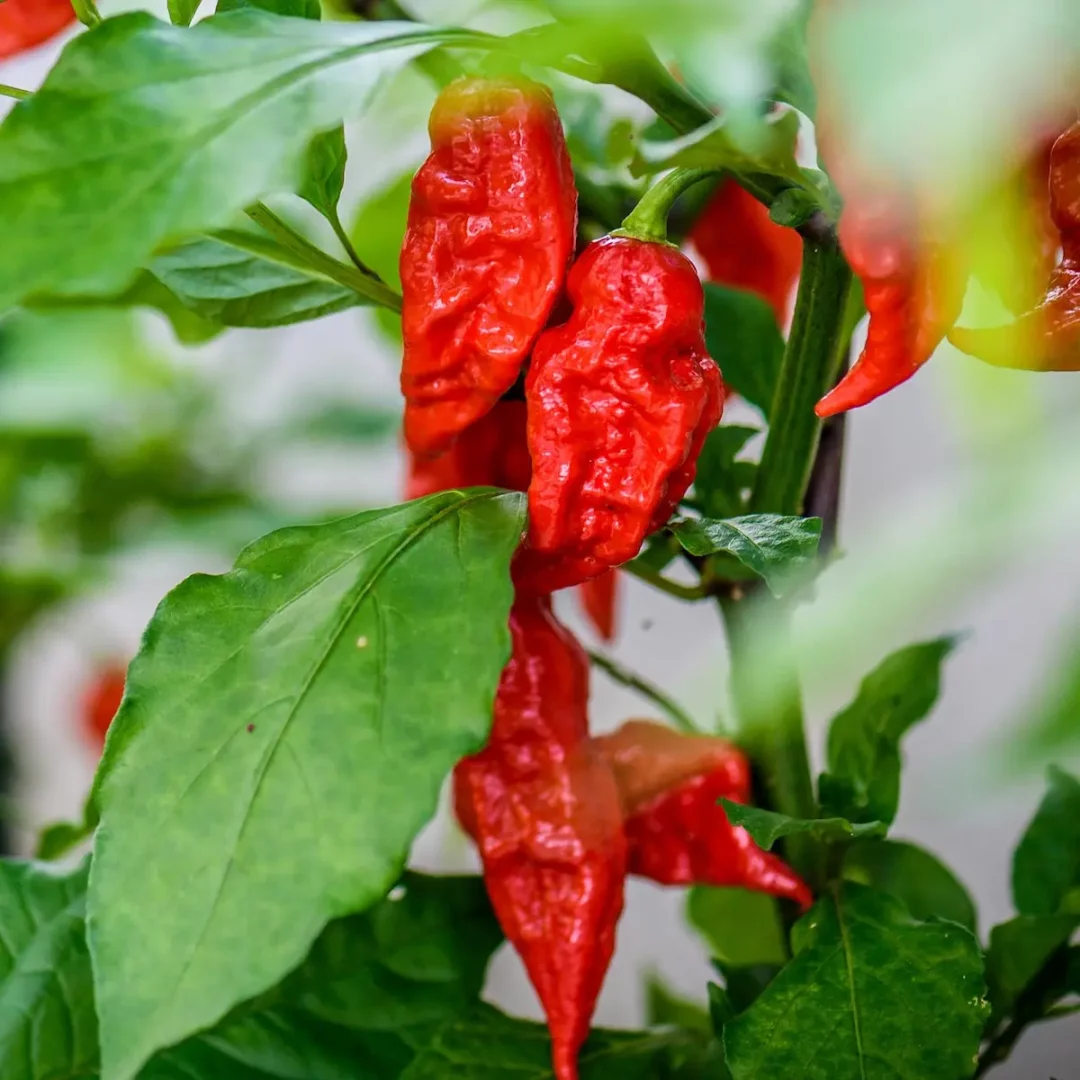

19. Trinidad Moruga Scorpion (Capsicum chinense)
Native to Trinidad and Tobago, the Trinidad Moruga Scorpion is one of the world’s hottest peppers, measuring over 2 million SHU. With a distinct scorpion-like tail and bright red color, it delivers an intense and lingering heat. Thriving in warm climates, these peppers require full sunlight and well-drained soil.
Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall. Used sparingly due to their extreme spiciness, Trinidad Moruga Scorpions are incorporated into hot sauces and spicy dishes, adding a potent kick that is not for the faint of heart.
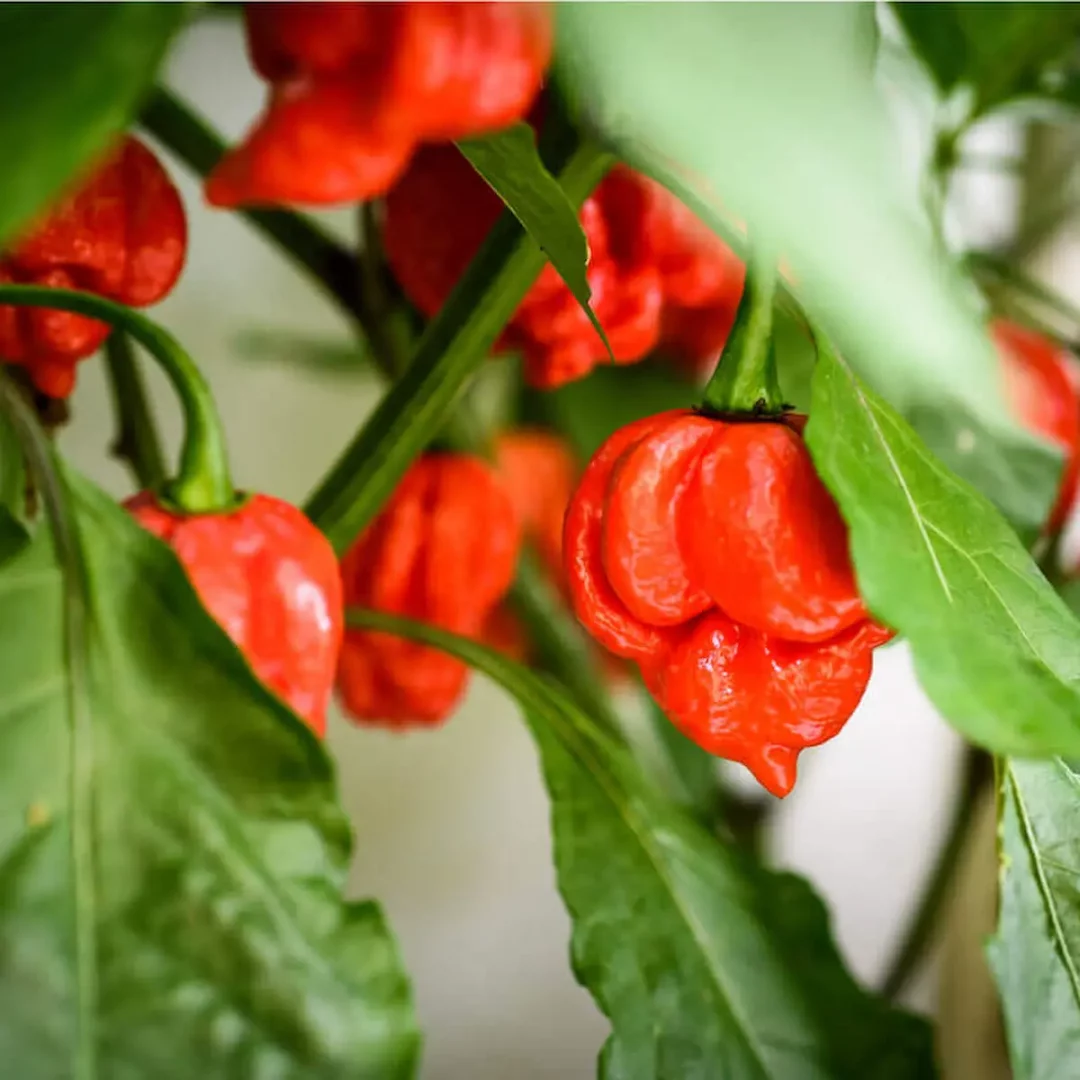

20. Paprika Pepper (Capsicum annuum)
Originating from Hungary, the Paprika Pepper is a sweet and mild variety, known for its vibrant red color. Measuring around 3 to 4 inches, it has a heat level ranging from 0 to 1,000 SHU.
Thriving in warm climates, Paprikas require full sunlight and well-drained soil. Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall. Paprika Peppers are dried and ground into a spice used in a variety of dishes, providing a sweet and smoky flavor to soups, stews, and Hungarian specialties.

21. Piquillo (Capsicum annuum)
Hailing from Spain, the Piquillo pepper is a sweet and mildly spicy variety, known for its small, triangular shape. Measuring around 2 to 3 inches, it has a heat level ranging from 0 to 1,000 SHU. Thriving in warm climates, Piquillos require full sunlight and well-drained soil.
Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall. Piquillo peppers are often roasted and used in various Spanish dishes, adding a smoky and slightly spicy flavor to tapenades, salads, and stuffed pepper dishes.

22. Cascabel (Capsicum annuum)
Originating from Mexico, the Cascabel pepper is a mild to moderately hot variety, known for its round shape and rattling sound when dried. Measuring around 1 to 2 inches, it has a heat level ranging from 1,500 to 3,000 SHU. Thriving in warm climates, Cascabels require full sunlight and well-drained soil. Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall. Used in Mexican cuisine, Cascabel peppers are often dried and ground into a spice, providing a warm and smoky flavor to salsas, sauces, and meat dishes.
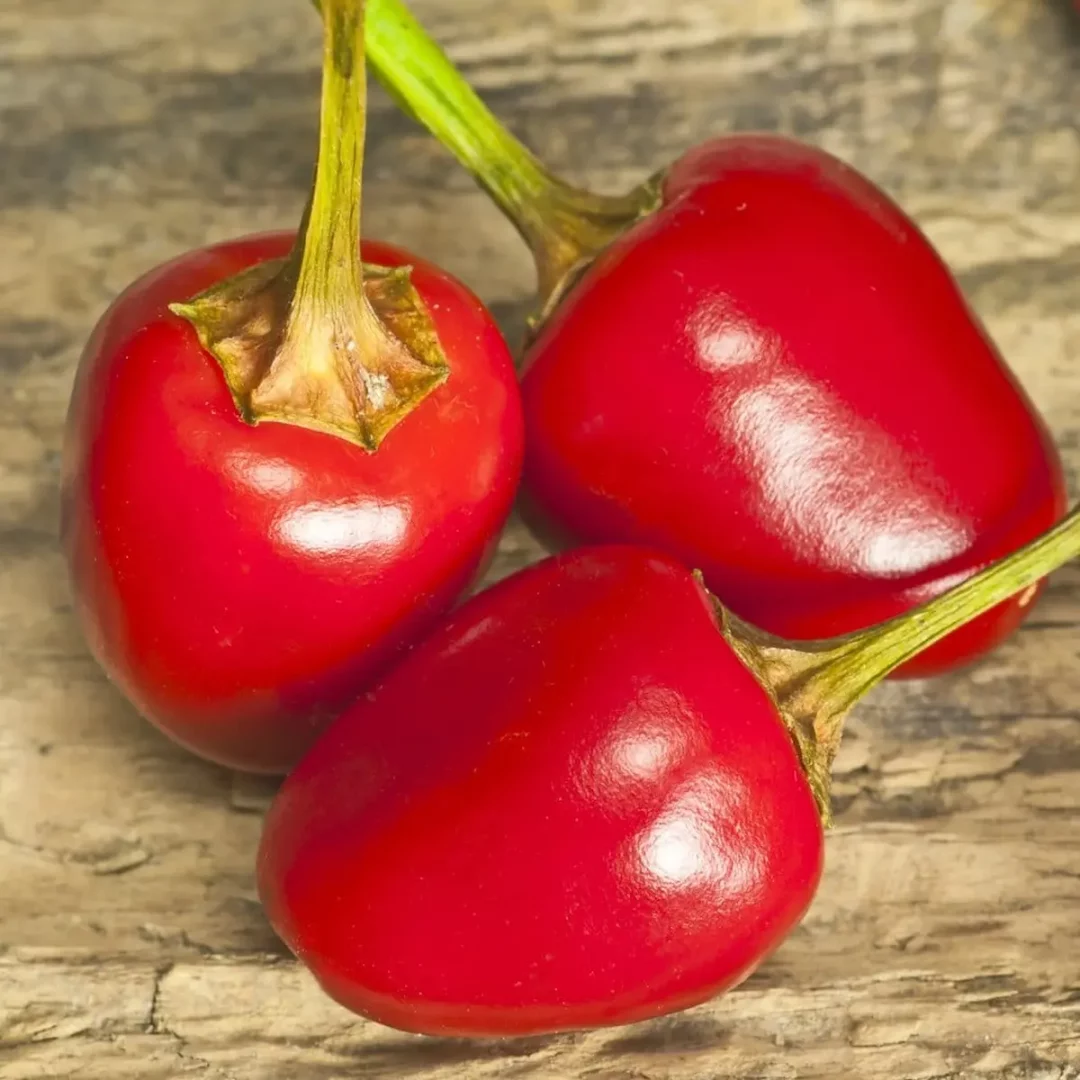

23. Pasilla de Oaxaca (Capsicum annuum)
Hailing from the Oaxaca region in Mexico, the Pasilla de Oaxaca pepper is known for its smoky flavor and medium heat level, ranging from 5,000 to 15,000 SHU.
With a slender and wrinkled appearance, it measures around 3 to 6 inches. Thriving in warm climates, Pasilla de Oaxacas require full sunlight and well-drained soil. Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall.
These peppers are often used in traditional Oaxacan dishes, providing a rich and smoky essence to moles, salsas, and other regional specialties.
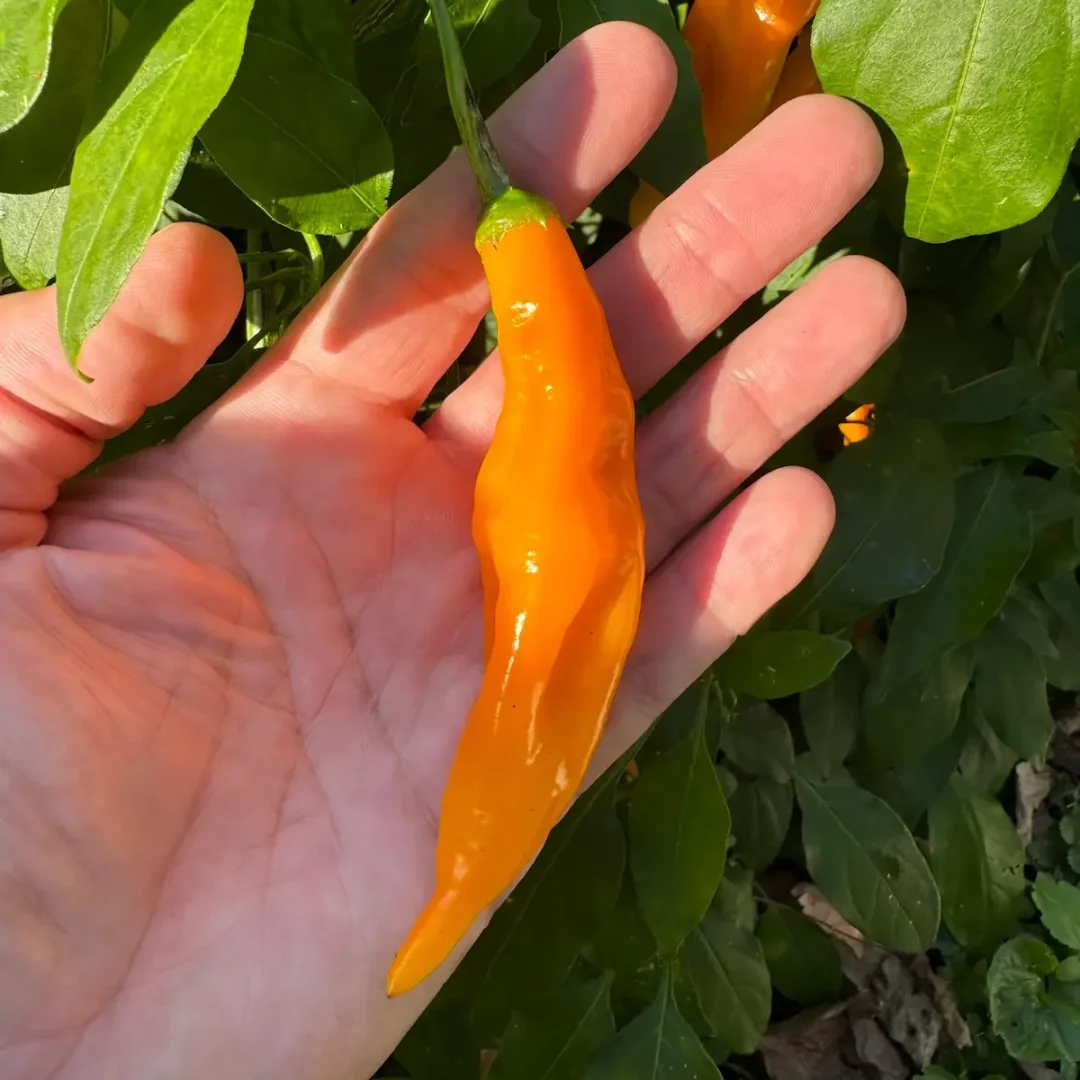

24. NuMex Twilight (Capsicum annuum)
The NuMex Twilight pepper, originating from the United States, is a small and ornamental variety known for its vibrant colors. Measuring around 1 inch, it has a heat level ranging from 30,000 to 50,000 SHU.
Adaptable to various cuisines, NuMex Twilights thrive in warm climates, requiring full sunlight and well-drained soil. Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall.
Often used for decorative purposes due to their colorful appearance, NuMex Twilights can also add a spicy kick to dishes, making them a unique and visually appealing choice for gardens and culinary creations.

25. Datil (Capsicum chinense)
Originating from the United States, specifically Florida, the Datil pepper is a hot and fruity variety, measuring around 2 inches. With a heat level ranging from 100,000 to 300,000 SHU, it is often used in hot sauces and marinades.
Thriving in warm climates, Datils require full sunlight and well-drained soil. Planting typically occurs in the spring, with harvesting extending from late summer to fall.
Known for its intense heat and unique flavor, the Datil pepper is a key ingredient in various Floridian dishes, providing a spicy kick to sauces, salsas, and seafood recipes.

Final Thoughts
In the diverse world of chili peppers, each variety contributes a unique flavor, heat level, and cultural significance to global cuisine. From the mild sweetness of Pimientos to the fiery intensity of Ghost Peppers, these peppers cater to a spectrum of tastes.
As culinary staples originating from various regions, they transform ordinary dishes into vibrant, spicy masterpieces. Whether enhancing the richness of Mexican mole sauces or elevating the heat in Thai curries, chili peppers continue to captivate taste buds worldwide.
The wide array of shapes, sizes, and heat profiles showcased by these peppers reflects their versatility and essential role in the art of cooking.
Related Articles
- Objects That Start With Z
- Cities That Start With Z
- Places That Start With Z
- Verbs That Start With Z
- Plants That Start With Z